# Docs
# What is sherpa.sh?
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
Welcome to Sherpa.sh - the world's lowest cost platform as a service
# What is Sherpa.sh?

Welcome! Sherpa.sh is the *worlds lowest cost platform as a service*. Our platform builds, deploys, routes, and scales your applications globally with 80% lower costs than competitors like Vercel and Netlify. We handle all the complications of configuring infrastructure for modern Javascript frameworks (Next.js, Sveltekit, Remix, [see our full list](/applications/supported-frameworks/)) and docker-based applications - including CDN, caching, edge functions, computing, DNS, and server management - so you can focus on writing code.
Think of us as an approachable, friendlier alternative to Vercel or Heroku. We're smaller, more personal, and handle all the server infrastructure so you can focus on your code - while giving you 5x the resources as those other providers for the same price!
## Jump right in
- **[Quickstart](/getting-started/quickstart)** - Deploy your first site in 2 minutes. Yes, it's that easy.
- **[SafetyNet](/infrastructure/safety-net)** - Gradually migrate with the security of having your existing provider always available as a fallback. Risk-free migration that instantly reduces costs.
- **[Supported Frameworks](/applications/supported-frameworks/)** - See our support frameworks and the ones we're adding soon.
- **[Continuous Delivery](/applications/continuous-delivery)** - Learn how we build and ship your code from a git push to production.
## FAQ
### How much does sherpa.sh cost?
Sherpa.sh offers flat-rate pricing with no charges for seats or projects. Just simple, predictable pricing that won't surprise you.
Our free plan offers the same resources as a Vercel Pro plan. Otherwise our paid plans start at $13.99/mo. This covers unlimited seats, unlimited projects, unlimited edge and origin function calls, and free migration.
Our fee is flat, meaning you can grow your team as large as you like, and never pay for extra seat. Our pricing is extremely competitive, most users get 5x the resources on sherpa.sh for the same price they were paying elsewhere.
You can view full pricing information on [our pricing page](https://sherpa.sh/pricing).
### How are sherpa.sh's costs so competitive?
We run our own servers for most services, instead of using cloud providers like AWS. This makes our costs ~10x less than the other providers who are wrapping AWS. By cutting out the cloud and running everything ourselves, we keep costs low and pass those savings on to you.
We've been running data centers for over 10 years and know most tricks to get the best server and bandwidth prices. If you want to learn about those tricks, check out our blog post about the hidden costs of web hosting. (coming soon)
### What frameworks do you support?
We are focused on supporting Javascript frameworks like: Next.js, Remix, Sveltekit, [and more](/applications/supported-frameworks/), along with all their advanced functionality like Partial Pre-rendering (PPR), Server Side Rendering (SSR), and Automatic Static Optimization (ASO).
Our [architecture](/infrastructure/architecture) is Kubernetes based, so we are not limited to JS projects only. We can deploy anything that runs in a Docker container: Python, Ruby, Laravel, etc.
See our full list of [supported frameworks](/applications/supported-frameworks/).
You can also [request support for a framework](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact) from inside the portal. If you ask, we will build it, and much quicker than you'd think!
### Why should I use Sherpa.sh?
Because you have better things to do than fiddling with server configurations or optimizing cloud spending. With sherpa.sh, it is easy to deploy your web app globally using best practices - without having to worry about surprise cloud bills.
You'll iterate faster with continuous deployment, save time you would have otherwise spent on DevOps, delight your users with incredible page-load speed, and if you ever run into road bumps you can get real help from a real person.
And since we skip the cloud middlemen, you'll be amazed at how affordable it all is.
### Can I migrate without downtime or risk?
Yes! Our [SafetyNet](/infrastructure/safety-net) feature lets you migrate to Sherpa.sh while keeping your existing provider (Vercel, Netlify, AWS, etc.) as an automatic fallback. If Sherpa.sh ever returns an error, your traffic instantly routes to your existing deployment - transparently to your users.
This means you start saving money immediately as Sherpa.sh handles your traffic, while your existing provider remains as a safety net. It's a zero-risk migration that also serves as ongoing disaster recovery. Once you're confident in your Sherpa.sh deployment, you can remove the fallback at any time.
# Continuous Delivery
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Continuous Delivery
Let's be honest - you didn't become a developer to wrestle with CI/CD pipelines. You want to be building amazing products, not debugging why your GitHub Action is suddenly taking 45 minutes to complete.
Instead of fiddling with deployment workflow, let sherpa.sh do all the heavy lifting for you. Just connect a Github repo and we'll handle the rest.
## Zero-Config Deployments
Link your GitHub repository, and you're done. No YAML files to configure, no build matrices to optimize, no runners to maintain. We automatically:
* Detect your framework and dependencies
* Configure optimal build settings (which you can [customize](/getting-started/configuration) as needed)
* Set up production-grade deployment pipelines
* Handle all the CI/CD infrastructure
## Anatomy of a Build
Every deployment follows a carefully orchestrated sequence of steps. Here's what happens behind the scenes:
#### 1. Creating Cache Storage
We maintain a globally distributed, high-performance caching layer. This layer is used by frameworks for ISR, PPR, and other caching functionality. This step allocates a slice of the caching layer for your application.
#### 2. Version Control Checkout
Shallow fetches your latest code from GitHub.
#### 3. Environment Configuration
Securely fetches your environment variables from our secrets vault and injects them into the build context.
#### 4. Dependency Installation
Installs your project dependencies based on your provided [build configuration](/getting-started/configuration).
#### 5. Project Build
Builds your application, optimizes assets, and prepares the production bundles.
:::note
During the build process all environment variables are located inside the locally written `.env` file (or .env.local or .env.production.local depending on your project setup).\
\
If you need to access these are parts of your build command (for javascript projects) be sure to use a package like `cross-env` to call your `package.json` commands so they have access to the environment variables.
:::
#### 6. CDN Asset Upload
Distributes your static assets across our global CDN network.
#### 7. Route Function Building
Compiles, optimizes, then containerizes your application's server-side components and API routes.
#### 8. Infrastructure Deployment
Provisions and configures the necessary cloud resources to run your application. We handle all the infrastructure heavy lifting, setting appropriate scaling rules and networking setup based on your selected plan.
#### 9. DNS Update
Once your application is live and static assets uploaded, its safe to update DNS records to point to the new deployment. If you are using a custom domain this is when it gets routed to your application - otherwise we use the default speficied in the [app configuration](/getting-started/configuration). We also provision SSL certificates using LetsEncrypt for your domain in this step. Doing this step ensures zero-downtime and a smooth cutover for every user.
## Deployment Triggers
Your code gets deployed automatically when:
* You push to your production branch
* A new pull request is opened
* New commits land on a PR branch
Each trigger spawns a deployment pipeline that handles everything from dependency installation to final deployment. No manual intervention required.
## Preview Environments
Surprises are for birthdays, not software. Every pull request gets its own complete preview environment. This means:
* Stakeholders can review changes on a real URL
* QA can test features in isolation
* You can catch issues before they hit production
* Each preview is an exact replica of what the branch would look like in production (yes, this means the build and deployment include your application [environment variables](/getting-started/configuration#environment-variables))
When a new pull request is opened it triggers a deployment of that branch. It will be available at the subdomain in your [app configuration](/getting-started/configuration) with the branch name appended. For example if your subdomain is set to `myapp.sherpa.software`and your branch name is `dev-feat-1` your feature branch will be available at `myapp-dev-feat-1.sherpa.software`.
Any new commits to a branch with an open pull request will also trigger a new deployment.
### Github Integration
When a new build is triggered - or a build completes - sherpa.sh will leave comments on the pull request with links to the most up to date information.
Deployments will also trigger build checks and github deployment objects to be created. Both will be updated based on the success/failure of the build.
## Instant Rollbacks
Made a mistake? No problem. Every deployment is immutable and cached globally. Rolling back is as simple as clicking a button in the "Deployments" tab.
To rollback (or promote a newer deployment):
1. Navigate to the Deployment table.
2. Search for the deployment you wish to rollback.
3. Click the Ellipse at the end of the table row
4. Click promote/rollback
:::note
**Environment Variables:** Previous deployments may not have the most up to date environment variables. Because some frameworks will embed the variables into the build output they cannot be updated new ones. If you need to rollback to a previous commit with new environment variables, we suggest pushing your current changes to a new branch, rolling back `Head` on the existing branch, then redeploying.
:::
:::caution
**Rollback Limitations:** In some cases you will not be able to rollback to your previous deployment. You should be aware of these scenarios:
1. You can only rollback to applications in the [configured region](/getting-started/configuration#app-region) for your application. For example, if your app settings currently target us-east, but your previous deployments are in us-west. You will not be able to rollback to them until you change your app settings back to us-west.
:::
1. Connect your GitHub repository (one click)
2. Add your environment variables
3. Push to your production branch
That's it. Seriously, we're not kidding. Here is the [quickstart](/getting-started/quickstart) docs.
Now, go build something awesome instead of babysitting your CI/CD pipeline!
# Promotions & Rollbacks
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Promotions & Rollbacks
Nothing stings quite like a broken production deployment. We've all been there – that late-night debugging and productino patching after a buggy release hits your users. Sherpa's deployment system was born to make those painful experiences a distant memory.
Our deployment system gives you:
* **Zero-downtime updates** - Your application stays available during deployments
* **Instant rollbacks** - Made a mistake? One click and you're back to safety
* **Progressive traffic shifting** - Test new versions with a portion of users before full commitment
* **Confidence in your deployments** - Know exactly what's happening at each step
We built this system because we were tired of deployment anxiety. The feeling of pushing code and holding your breath isn't sustainable. Your deployments should be boring (in a good way).
### How Sherpa Deployments Work
#### The Basics: Green-Green Deployments
Sherpa uses a "green-green" deployment strategy. Unlike blue-green deployments where you maintain two environments, we dynamically create new instances while keeping existing ones running.
Here's the flow:
1. You push new code to your repository
2. Sherpa creates a new containers in our k8s clusters with your changes
3. Both your current and new code run simultaneously (both green!)
4. Traffic gradually shifts to the new version after health checks pass
5. Once fully shifted, old instances are gracefully terminated
This approach means you always have a healthy system running, with controlled traffic management between versions.
#### Health Verification
Sherpa won't route traffic to unhealthy instances. We rigorously check:
* **Readiness probes**: Verify if your application is ready to receive traffic
* **Liveness probes**: Continuously monitor if your application is healthy
* **Startup probes**: Check if your application has started successfully
:::note
Currently, all probes are directed to "/" of your application. A future release will allow you to customize this variable.
:::
Only when all health checks pass does Sherpa consider your deployment ready for traffic.
### The Developer Experience
#### Promoting a Deployment
Promoting a deployment with Sherpa is straightforward, just merge your branch into production on Github. Sherpa.sh will automatically pick up the change and create a new deployment to promote.
#### Rollbacks: Your SafetyNet
Sometimes things go wrong - and that's okay. Sherpa's rollback is immediate:
1. Navigate to your project's deployment history
2. Click "Rollback" on any previous successful deployment
3. Traffic instantly returns to the previous version
Your users won't even notice there was an issue. That's the point.
:::caution
Domain settings control ingress separate from your deployements. Be careful changing url settings post-deployment if you plan to do rollbacks to deployments from long ago.
So, If you changed your domain settings (updated the url) of your application, you may experience issues rolling back to a deployment before you chaned the url settings.
For example: Nextjs projects has a asset prefix setting that tells nextjs what url to find your static assets. If you're previous deployment has assets at myproject.example.com and you changed your url to hello.example.com. If you rollback to the deployment with myproject.example.com, the myproject url will still be in your deployments code and that url will no longer resolve. Because it's now set to hello.example.com.
:::
### Future Features
In the future we plan to support multiple promotion strategies beyond "green green" including:
* **Green Green**: Switch all traffic immediately when pod is ready
* **Canary**: Gradually shift traffic based on a timeline (10% → 50% → 100%)
* **Scheduled**: Set a specific time for promotion
* **Split:** Send a % of traffic to the new deployment until ready to promote all traffic.
* **Other:** Have a unique request? Contact us below.
If you would like to see this implemented sooner than later, please [contact us](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact).
# Securing your App
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Securing your Application
At Sherpa.sh, we take security seriously. This document outlines our recommended security practices and integrations to help you protect your applications and infrastructure from common threats. Following these guidelines will help ensure your projects deployed through Sherpa.sh remain secure and reliable.
### Sherpa.sh Infrastructure Security
At Sherpa.sh, we maintain robust security across all infrastructure layers to provide you with a secure platform for your applications. These are things sherpa.sh takes care of for you, that you would have to do if you had your own servers (using something like Coolify or Dokku). Our comprehensive approach includes:
1. **Operating System Security**
* Regular patching and updates for all server operating systems
* Principle of least privilege for system access
* Regular security scans and vulnerability assessments
2. **Network Security**
* Network segmentation to isolate critical systems
* DDoS protection at the edge
* Real-time network monitoring for suspicious activity
3. **SSL/TLS Implementation**
* TLS 1.3 and strong cipher suites enforced
* Automatic certificate rotation before expiration
* HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) enabled by default
4. **Data Protection**
* Encryption of all data in transit
* Secure backup systems with encryption
* Data isolation between customers
5. **Continuous Security Monitoring**
* 24/7 monitoring of all infrastructure components
* Automated alerts for security anomalies
* Incident response team on standby
We manage these security measures behind the scenes so you can focus on developing your applications without worrying about infrastructure security. This approach allows us to maintain a secure environment while providing the flexibility and resources you need for your projects.
### Sherpa.sh Platform Security Best Practices
#### Secure Your Account
1. **Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)**
* Enable 2FA on your Sherpa.sh account immediately to prevent unauthorized access
* Use an authenticator app (like Google Authenticator or Authy) rather than SMS when possible
* Store recovery codes securely in a password manager or other secure location
2. **Strong Password Practices**
* Use a unique, complex password for your Sherpa.sh account
* Change your password periodically, especially after suspected security incidents
#### Environment Variables and Secrets Management
1. **Never Commit Secrets to Your Repository**
* Store sensitive information like API keys, database credentials, and access tokens as [environment variables](#environment-variables-and-secrets-management) in Sherpa.sh
2. **Secure Environment Variable Handling**
* Use the principle of least privilege - only expose variables to services that need them
#### GitHub Repository Security
1. **Enable Branch Protection Rules**
* Navigate to your repository on GitHub → Settings → Branches → Add rule
* Protect your main/production branch with these settings:
* Require pull request reviews before merging
* Require status checks to pass before merging
* Require signed commits
* Do not allow bypassing the above settings
* [GitHub Branch Protection Documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/configuring-branches-and-merges-in-your-repository/managing-protected-branches/managing-a-branch-protection-rule)
2. **Limit Repository Access**
* Review collaborators regularly and remove unnecessary access
* Use teams with appropriate permission levels instead of individual access
* Consider implementing a CODEOWNERS file to ensure proper code review coverage
3. **Secure Continuous Integration/Deployment**
* Implement security scanning in your CI/CD pipeline
* Scan dependencies for vulnerabilities before deployment
* Consider implementing automated security testing
#### Application Hardening
1. **Regular Security Updates**
* Keep all frameworks and libraries up-to-date
* Subscribe to security bulletins for your technology stack
2. **Security Headers and Configuration**
* Set appropriate security headers like Content-Security-Policy, X-XSS-Protection, etc.
* Configure proper CORS settings to restrict cross-origin requests
* Implement proper input validation and sanitization
* Enable CSRF protection for all forms
### Additional Application Protection with Arcjet
If you want additional application security, we recommend using [Arcjet](https://arcjet.com) in your project.
#### Why Arcjet?
Arcjet has been architected around a few key principles:
* Security protections are placed alongside the code they're protecting, ensuring full application context
* Security rules are easy to test in both development and production environments
* Integration is simple, adds minimal latency, and requires no architectural changes
#### Core Security Features
Arcjet provides several key security primitives that can be used independently or combined:
1. **Shield** - Protection against common attacks, including those in the OWASP Top 10
2. **Rate Limiting** - Control the number of requests from a client over a time period
3. **Bot Protection** - Detect and block automated clients, including AI scrapers
4. **Email Validation & Verification** - Verify email address validity
5. **Sensitive Information Protection** - Prevent unwanted PII submission
To learn more about Arcjet's security features, visit [their documentation](https://docs.arcjet.com/).
### Security Updates and Support
For security concerns or questions, please contact our security team at [security@sherpa.sh](mailto:security@sherpa.sh).
# Supported Frameworks
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Supported Frameworks
## Framework Support
The sherpa.software platform is designed to accommodate a wide variety of frameworks, leveraging framework defined architectures to maximize the benefits specific to each. This ensures a seamless deployment experience and optimized performance for your application.
In other words: Get blazing fast performance without a lifting a finger.
## Supported Frameworks
Explore the frameworks currently supported by sherpa.software below, or in the sidebar to the left. We're working hard to add more. If you need something specific reach out to us, and we will fast track it!
### [Astro](/supported-frameworks/astro)
Lightning-fast static sites with islands architecture. Ship less JavaScript with partial hydration and zero-config deployments.
### [Docker](/supported-frameworks/docker)
Django, Rails, Laravel... anything that goes in docker can be launched by sherpa.software.
### [Next.js](/supported-frameworks/nextjs)
Get all the benefits of framework defined architecture. ISR, PPR, AGO, SSR, and more.
### [Nuxt](/supported-frameworks/nuxtjs)
Nitro speed deployments of Fullstack Vue projects build with Nuxt. No edge request fees, and faster page loads.
### [Payload CMS](/supported-frameworks/payload-cms)
Powerful headless CMS with instant scaling, zero maintenance, and built-in security on sherpa.software.
### [React](/supported-frameworks/react)
Build & Ship your React assets around the world.
### [Remix](/supported-frameworks/remix)
Zero-config Deployments of Fullstack and SSG Remix applications. Native support = seamless experience.
### [Sveltekit](/supported-frameworks/sveltekit)
Fast builds, small bundles, and simple deployment with support for SSR, SPA, PWA, and more.
### [Custom Setup](/supported-frameworks/custom-setups)
Have a unique need? HIPAA, FedRAMP, Micro-services, video streaming? We can help.
---
:::tip
We support most of the [AI Website Builders](/supported-frameworks/supported-ai-website-builders) like Lovable and Bolt. When you are ready to go to production with your AI app, sherpa.software is the fastest way to get to production.
:::
:::note
We support both ESM & Common JS module systems - as well as Typescript projects.
If for some reason you have a project that relies on Asynchronous Module Definitions (AMD), it will need upgrading to work on sherpa.software. Reach out if you need assistance or have a special request.
:::
## Request a Framework
If your preferred framework isn't listed in our [framework roadmap](#framework-roadmap). Please, [submit a request](https://www.sherpa.software/contact) for additional frameworks. We are working hard to expand our offerings based on user feedback.
Seriously, send us a message! We'll add your framework faster than you'd think!
## Framework Roadmap
Below you will find a list of frameworks we are working on supporting. If we need to add something else to this list - or implement a specific one sooner - [let us know](https://www.sherpa.software/contact)!
* [x] Next.js
* [x] React
* [x] Any Docker Container
* [x] create-react-app
* [x] PayloadCMS
* [x] Remix
* [x] Astro
* [ ] Gatsby
* [x] nuxt.js
* [x] vue.js
* [x] Sveltekit
* [x] Svelte
* [ ] Angular
* [ ] Solidjs
* [ ] Qwik
* [ ] Dino
* [ ] Your framework here (or higher!) - [let us know](https://www.sherpa.software/contact/)!
# v0.1.0 - 21/03/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
March 21, 2025
# v0.1.0 - 21/03/25
This update introduces several new features and improvements aimed at enhancing deployment capabilities and user experience. Key features include support for deploying Docker containers, improved DNS routing options, and embedded user guides. Enhancements focus on expanded logging functions, decoupled ingress management for flexible deployments, and enhanced error messaging for ESM projects. Additionally, navigation within the project settings is streamlined. Bug fixes are addressed to improve overall system stability and functionality.
## New Features
* Docker containers: Deploy any docker container application. It is automatically put behind a CDN, given an SSL certificate, and configured for horizontal autoscaling.
* DNS Routing: After routing your domain to the sherpa.sh nameservers you can create and manage your DNS records from the domain detail page.
* Manual DNS Routing: If you cannot route your nameservers to sherpa, you can now manually create CNAME records on your provider to route your domain to your sherpa.sh project.
* We've created our [first training video](../../training-videos/deploying-your-first-application). These will be embedded in the site to improve the experience and help users.
## Improvements
* ESM projects with build errors now have more verbose messaging
* Logging is moved to its own dedicated page instead of living under each deployment. View the CDN logs as well as your application console output.
* Backend change: Decoupled ingress from deployments. This gives us greater control and flexibility in managing routes and unlocks more complicated deployment strategies. Whenever you change your domain settings, the new url will automatically be generated and applied to your application.
* Add logging and deployment links to the sidebars in project settings, as well as in the individual deployment detail pages. This makes navigation easier.
## Bug Fixes
* When changing an application framework (from nextjs to docker for example) those changes broke the connection between logs and the deployment. This is fixed.
* Branch deployment links not being saved and linked to the GUI despite being deployed. This is fixed.
* In some instances deployments were not getting their preview / production badges tagged appropriately due to a race condition. This prevented rollbacks as well as log monitoring. This is now patched.
* CommonJS projects not utilizing cjs file extensions for the next config file would result in a build error. This has been patch, and now CommonJS projects support all valid extension types (cjs, js, ts)
* Fix environment variable bug where you cannot save if one of the env keys has an invalid character.
* Fix Github integration where some projects won't receive active links on the the PR comment.
* Branches with "/" or "." would cause URL errors on ingress controllers. We now replace non-compatible characters in branch names with urls to hyphens to make url compatible. And any periods are replaced with hyphens as well so the branch name is all a single subdomain compatible with the wildcard SSL cert.
* Ignore eslint and other type/format checkers in our custom cache handler and next config files when compiling.
* Only allow root domains in the new domain form. Limit to 63 characters per part to comply with RFC 1035
# App Environments
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# App Environments: Prod/Staging/Dev/Multi-tenant
Create and manage unlimited staging, testing, and production environments for your Sherpa.sh applications with branch-based deployments and environment-specific configurations.
### Overview
When you import a project to Sherpa.sh, a default **Production** environment is automatically created from your repository's default branch (typically `main` or `master`). You can create unlimited additional environments on any paid plan, each with its own configuration, environment variables, and deployment settings.
#### Key Benefits
* **Unlimited Environments**: Unlike other platforms that charge per environment, Sherpa.sh includes unlimited environments on all paid plans
* **Branch-Based Deployments**: Each environment deploys from a specific branch in your repository
* **Isolated Configurations**: Each environment maintains its own environment variables and settings
* **Automatic Deployments**: Configure automatic deployments on commits or pull requests
* **Custom Domains**: Each environment gets a unique subdomain on sherpa.software plus support for custom domains
### Creating a New Environment
Follow these steps to create additional environments for your application:
#### Step 1: Navigate to Applications Page
From your application dashboard, click the **"New Environment"** button on the Applications page.
#### Step 2: Configure Environment Settings
Name your environment and select the branch you want to deploy from:
* **Environment Name**: Choose a descriptive name (e.g., `staging`, `testing`, `development`)
* **Source Branch**: Select the Git branch this environment will track and deploy from
#### Step 3: Add Environment Variables
Configure [environment-specific variables](/getting-started/configuration#environment-variables) for your new environment:
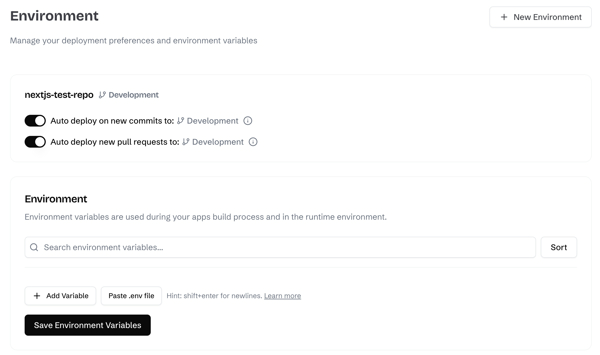
#### Step 4: Deploy
Your environment is now ready to deploy! Click **"Start New Deployment"** to trigger your first deployment.
### Multi-Tenancy Configuration
> **🏢 Multi-Tenancy Use Case**: Deploy multiple isolated instances of your application for different clients using environment-specific configurations.
Sherpa.sh's unlimited environments make it ideal for multi-tenant applications. Create separate production environments for each tenant with isolated configurations:
#### Example: Multi-Tenant SaaS Setup
Each tenant environment:
* Deploys from the same codebase ( `main` branch)
* Maintains completely isolated data and configurations for each customer (`customer-1`, `customer-2`, `customer-3`)
* Can have custom domains (customer1.yourapp.com, customer2.yourapp.com, customer3.yourapp.com)
* Updates simultaneously when you push to main
### Common Environment Patterns
#### Standard Development Workflow
```
main branch → Production Environment
develop branch → Staging Environment
feature/* branches → Development/Testing Environments
```
#### GitFlow Pattern
```
main branch → Production
release/* branches → Staging
develop branch → Development
hotfix/* branches → Hotfix Environment
```
### Best Practices
1. **Environment Naming**: Use clear, consistent naming conventions (`production`, `staging`, `testing`, `dev-john`)
2. **Variable Management**: Never commit sensitive environment variables to your repository. Use Sherpa.sh's environment variable interface.
3. **Branch Protection**: Set up branch protection rules in your Git provider to prevent accidental pushes to production branches.
4. **Testing Pipeline**: Create a testing environment that automatically deploys pull requests for QA review.
5. **Rollback Strategy**: Keep staging environments on the same deployment schedule as production for accurate testing.
# Debugging
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Debugging
Below you will find common error scenarios and how to debug them.
## Build process
### Yarn: The lockfile would have been modified by this install, which is explicitly forbidden
If during the install process your receive the error message: `The lockfile would have been modified by this install, which is explicitly forbidden` this is because the lockfile in your repository doesn't match the dependencies in your package.json file. You have two options for fixing this:
1. Update your repo so that the lockfile matches your dependencies.
2. Change your install command from `yarn install` to `yarn install --no-immutable`
Either option will resolve your error and allow the package installation to complete successfully.
### Node GYP Errors
Node-gyp errors occur when native Node.js modules compiled for one system architecture don't match your current environment. This commonly happens with modules like Sharp, bcrypt, or sqlite3 when moving between different operating systems, CPU architectures (x86 vs ARM), or Node.js versions. On sherpa.sh your project is build inside an Alpine Linux container running on x86 architecture.
When native module installation fails during `npm install`, preventing your build from completing at all, using the install flag `--ignore-scripts` skips postinstall scripts that often handle native module compilation.
Then you can manually rebuild for your architecture with the `npm rebuild` command.
#### Example
```bash
# Failing build command
npm i
# Working build command
npm i --ignore-scripts && npm rebuild
```
### Missing a dependency during install command
When a new deployment is triggered your project is built inside a docker container. This docker container is an alpine linux distribution with predefined packages installed. If you receive an error about a missing package during a build, it is likely because it is not included by default in our docker image.\
\
The following packages are installed by default:
```
RUN apk add --no-cache
bash \
curl \
nodejs \
npm \
python3 \
make \
g++ \
build-base \
gcompat \
linux-headers \
openssl-dev \
musl-dev \
libc-dev \
zlib-dev \
pkgconfig \
git
```
If you are in need of a package not listed above during the build process. Please [let us know in discord](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy) and we will add it for you. Or you can append `apk add [PACKAGE] &&` to your build command.
### ESLint errors during build command
If you have eslint enabled lint errors will cause a build to fail. You can either fix your linting errors then commit your changes or disable ESLint.
The method to disable ESLint during your build process depends on the framework or toolchain you are using. Here are some common approaches:
### Summary Table
| Framework/Tool | How to Disable ESLint During Build |
| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Create React App | Set `DISABLE_ESLINT_PLUGIN=true` in `.env` or script |
| Next.js | Set `{eslint: {ignoreDuringBuilds: true}}` in `next.config.js` |
| Other/Custom | Remove ESLint from build config or delete ESLint-related files. |
**Note:** Disabling ESLint during builds is generally not recommended unless you have linting handled elsewhere as it may allow code quality issues to slip into production.
### JNLP4 Connect Timeout / Javascript heap out of memory
This occurs when you're build project has run out of memory. The solution is to either reduce the memory used during your build process OR to upgrade to a dedicated build server.
#### Sentry Source Maps
Sentry source maps can consume a significant amount of memory, even for small to medium-sized projects. This can be problematic if upgrading to a dedicated build server is not feasible.
To mitigate this issue, you can disable source maps in production. In a Next.js application, you can achieve this by modifying your `next.config.js`:
```javascript
module.exports = withSentryConfig{
config,
sourcemaps: {
disable: true,
},
};
```
By setting `sourcemaps.disable` to `false`, you prevent the generation of source maps in the build process, thereby reducing memory usage during the build process.
### Failed to compute cache key during container build
The error message likely indicates that the directory specified for the output is incorrect or does not exist. In this case, `"/baddir"` is likely not the directory where your build command outputs files. The "failed to calculate checksum" part of the error means that the system cannot find this directory to proceed with the build. Make sure to verify and correct the output directory in your [build settings](/getting-started/configuration).
```
ERROR: failed to build: failed to solve: failed to compute cache key: failed to calculate checksum of ref vxd2szn1mu5hcxp86ikag4uei::ia0osmeodh7hzb4n6p9iffjg9: "/baddir": not found
script returned exit code 1
```
### ERROR! Directory does not exist
This typically occurs when building projects using [SSG (Static Site Generation)](/getting-started/configuration#static-generation-only) and your project outputs to a different directory during build that what you have set for your [output directory in the your build settings](/getting-started/configuration#output-directory).
To debug this, run your build command locally and see where your folder is output to, and confirm that it matches the directory in your build settings.
## Runtime Errors
### Module not found errors
This is typically due to missing binaries.
Next.js offers an optimized “standalone” output (by setting `output: "standalone"` in `next.config.js`) specifically for Docker/container deployments.
* The “standalone” build traces all runtime dependencies and bundles the minimal required Node modules and files for production runtime into `.next/standalone`.
* For a production Docker image, you only need to copy the content of `.next/standalone`, `.next/static`, and `/public` (and related assets) into a lightweight Node.js base image.
* System-level Ubuntu packages are usually **not needed at runtime** if everything was bundled and compiled during the build phase, _unless_ your app directly uses OS libraries at runtime (which is rare for most web apps).
\
## Url doesn't display your app
### 502 Error when visiting your application
This error means there is a bug in your application that is preventing it from starting. The first thing you should do is check your application logs in the dashboard.
1. First navigate to logs
2. Select your application and environment then click **console logs** to get the output from your application
From here you should see the message, and begin debugging. Good first steps are to copy your environment variables locally and try to replicate the issue on your local machine (make sure to use the same build and run commands you use in Sherpa.sh)
If you are deploying a docker project, please try building then running your docker container locally using this command (be sure to use the same Dockerfile you set in the Sherpa.sh portal):
:::note
Make sure you have a `.env`file in directory you run this command. This should contain the environment variables you have set for your application in the sherpa.sh dashboard.
:::
Then running it using this command:
```
docker run --env-file .env local-test/my-project:latest
```
If you project runs locally this way, it should work on sherpa.sh and you'll stop experiencing the 502 error.
### 500 Error when visiting your application
This is likely due to a bug in your app, or a misconfigured environment variable. The first step is to check your logs in the sherpa.sh portal. Visit the **Logs** page then select your project and deployment. Once you've selected the offending deployment in the tab filters in the upper right select "**Application Console**". Here you will see the most recent logs from your application - which likely will contain the source of the error.
### 400 Request Header or Cookie Too Large
This error occurs when the size of the request headers sent to the backend exceed the allowed limits. Specifically, individual request headers must not exceed 16 KB, and the combined size of all headers, including the header names, must not exceed 32 KB. This keeps memory resources effecient and your app serving request with low latency.
This issue often arises from excessively large headers in a request. On Sherpa.sh, applications may have custom headers, which, if overly large, can trigger this error during server request processing.
To troubleshoot this error, follow these steps:
1. Limit header size: Ensure that the size of each request header does not exceed 16 KB
2. Manage total header size: Monitor and control the combined size of all headers, keeping it under 32 KB
3. Review cookies: Since cookies are included in the header, it's crucial to limit their size as part of the overall header size
## Content issues after a successful deployment
### Static assets get (blocked:csp) error
Your `Content-Security-Policy` on static assets is likely mapped only to self. Sherpa.sh uses a separate url for static assets to improve performance. Our deployment process typically overrides these settings. But if you have a custom setup in your projects, you will need to update the content security policy to allow all urls on your root domain.
### SSL Certificate Issue.
If you have a cert issue, or receive net::ERR\_CERT\_COMMON\_NAME\_INVALID. There are usually one of two causes.
1. You have the wrong DNS records set. If using a custom domain, check that you have properly routed your [Custom Domain](/getting-started/custom-domains) with the proper DNS records
2. Your Cert didn't get picked up by the deployment. This can happen if you deploy before a cert is validated, while changing setting during deployment, and a few other cases. If this happens - redeploy your project and it will pick up your certificate.
If you still have issues. Please visit our Discord and open a ticket.
### This site can't be reached. Server IP address could not be found.
While rare, this can happen to deployments that are in progress during an infrastructure upgrade. If you have this issue, redeploy your project and it will pick up the IP.\
\
If you still have issues after redeploying, please visit our Discord and open a ticket.
# Runtime Environment
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Runtime Environment
How Sherpa.sh handles OS-level dependencies and runtime environments for your applications.
### Dependency Management
**Automatic Dependency Installation** When you deploy a project, Sherpa.sh automatically detects your package manager and installs all dependencies listed in your `package.json`, `yarn.lock`, `pnpm-lock.yaml`, `bun` or other lock files. This ensures all Node modules and JavaScript dependencies are available during build and runtime.
**Custom Install Commands** Configure custom installation commands in your [project settings](/getting-started/configuration) for specialized dependency requirements or multi-step installation processes.
### OS-Level Dependencies
**Build Infrastructure** Sherpa.sh runs builds and deployments within the standard [node-slim docker images](https://hub.docker.com/_/node). We additionally include essential system libraries and tools required for most Node.js and web projects. Build enviroments always use the latest node LTS. The final deployed container contains the version you select in[ application settings](/getting-started/configuration#nodejs-version)
**Native Module Support** Node modules requiring compilation or native binaries (such as `sharp`, `sqlite3`, `canvas`) are automatically built during deployment. Sherpa.sh ensures these binaries are compiled against the same runtime environment where your application executes, eliminating common deployment issues.
### System Libraries
**Pre-installed Libraries** The Sherpa.sh runtime includes commonly-used system libraries needed by popular frameworks and tools:
#### Core Development Tools
```bash
# Build essentials
build-essential, gcc, g++, make, cmake
autoconf, automake, libtool, nasm, pkg-config
# Version control and utilities
git, curl, wget, bash, unzip
```
#### Image Processing Libraries
```bash
# Image manipulation (Sharp, Canvas support)
libvips-dev, libvips-tools
libpng-dev, libjpeg-dev, libwebp-dev
libgif-dev, libtiff-dev, librsvg2-dev
libcairo2-dev, libpango1.0-dev, libpixman-1-dev
```
#### Database Client Libraries
```bash
# Database connectivity
libpq-dev # PostgreSQL
libmysqlclient-dev # MySQL
libsqlite3-dev # SQLite
```
#### Browser Testing Support
```bash
# Headless browser libraries (Puppeteer, Playwright)
libgtk-3-dev, libgbm-dev, libxrandr2
libxcomposite1, libxcursor1, libxdamage1
libnss3, libcups2, libdrm2
```
#### Security and Compression
```bash
# SSL/TLS and compression
libssl-dev, libffi-dev
zlib1g-dev, libbz2-dev
```
### Runtime Environment Characteristics
**Python Support** Python 3 is included with development headers for native module compilation:
```bash
python3, python3-pip, python3-dev
python-is-python3 # python command points to python3
```
**Consistent Build and Runtime** Applications build and execute in identical container environments, ensuring binary compatibility and reducing runtime errors from missing libraries or version mismatches.
### Limitations and Workarounds
**System Library Constraints** The runtime environment uses a fixed set of system libraries. If your application requires specialized system packages not included in the base image, consider these alternatives:
1. **Find npm alternatives**: Look for JavaScript implementations of native tools
2. **Use included libraries**: Leverage the comprehensive set of pre-installed packages
3. **Custom functions**: Implement workarounds using available system tools
4. **Reach out to support:** Head into [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh) and request a new package be added to the runtime.
**Supported Use Cases** The runtime environment supports most common development scenarios:
* Image processing and manipulation
* Database connectivity (PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite)
* Headless browser automation
* Cryptographic operations
* File compression and archives
### Best Practices
**Dependency Optimization**
* Use lock files (`package-lock.json`, `yarn.lock`) for reproducible builds
* Specify exact versions for critical dependencies
* Test locally with similar Node.js versions
**Native Module Compatibility**
* Verify native modules support Linux x64 architecture
* Use modules with prebuilt binaries when possible
* Test deployment with native dependencies in staging environment
**Performance Considerations**
* Minimize dependency installation time with `.npmrc` configuration
* Use `npm ci` for faster, reliable installs in production
* Cache dependencies when possible using build optimization settings
The Sherpa.sh runtime environment provides a robust, predictable foundation for deploying Node.js applications with complex dependencies while maintaining security and performance standards.
# Cronjobs
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Cronjobs
### Overview
Scheduled background tasks (cron jobs) are essential for automating recurring operations in your application. This guide covers implementation approaches for containerized applications deployed on the Sherpa.sh platform.
### How Cron Jobs Work on Sherpa.sh
#### Platform Architecture
On Sherpa.sh, your applications run as containerized workloads managed by Kubernetes clusters. This architecture provides the perfect foundation for running reliable background cron jobs alongside your web application.
**Key Platform Benefits:**
* **Automatic Scaling**: Kubernetes automatically scales your containers based on resource usage
* **High Availability**: Multiple redundant control planes ensure your cron jobs continue running
* **Container Isolation**: Jobs run in identical environments across all instances
* **Global Distribution**: Jobs can run across multiple regions for reliability
#### Deployment Model
Your application is deployed as a Docker container with the following characteristics:
* **Single Container**: Both your web server and cron jobs run in the same container instance
* **Persistent Process**: The container's entrypoint keeps both services running simultaneously
* **Shared Resources**: Web requests and background jobs share the same application context
* **Auto-restart**: Kubernetes automatically restarts containers if they fail
#### Request vs Background Job Execution
Understanding the execution model is crucial for proper cron job implementation:
| Execution Type | Timeout Limit | Use Case |
| --------------- | ------------- | --------------------------------- |
| HTTP Requests | 60 seconds | API endpoints, page rendering |
| Background Jobs | Indefinite | Data processing, cleanup, reports |
This means your cron jobs can run for hours while HTTP requests are capped at 60 seconds.
### Quick Setup Guide
#### Step 1: Configure Your Container Entrypoint
Structure your application to handle both web traffic and scheduled tasks:
```javascript
// server.js - Main application entry point
const express = require('express');
const cron = require('node-cron');
const app = express();
// Web server setup
app.use(express.json());
app.get('/health', (req, res) => {
res.json({ status: 'healthy', timestamp: new Date().toISOString() });
});
// Initialize cron jobs
function initializeCronJobs() {
// Daily cleanup at 2 AM UTC
cron.schedule('0 2 * * *', async () => {
console.log('Starting daily cleanup...');
await performDailyCleanup();
});
// Hourly health check
cron.schedule('0 * * * *', async () => {
await performHealthCheck();
});
console.log('Cron jobs initialized');
}
// Start both web server and cron jobs
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
initializeCronJobs
```
#### Step 2: Update Your Dockerfile
Ensure your container is configured for long-running processes:
```dockerfile
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
# Install dependencies
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
# Copy application code
COPY . .
# Expose port for web traffic
EXPOSE 3000
# Start both web server and cron jobs
CMD ["node", "server.js"]
```
#### Step 3: Deploy to Sherpa.sh
Deploy your application normally - the platform will automatically:
* Build your Docker container
* Deploy to Kubernetes clusters
* Start your web server and cron jobs
* Scale based on traffic and resource usage
### Implementation Strategies
### Prerequisites
* Active Sherpa.sh account
* Supported runtime: Node.js, Python, Go, or other containerized applications
* Git repository connected to Sherpa.sh
* Basic understanding of cron syntax
### Platform-Specific Considerations
#### Resource Management
Your cron jobs share resources with your web application. Monitor memory and CPU usage to ensure optimal performance:
```javascript
// Monitor resource usage in cron jobs
cron.schedule('0 1 * * *', async () => {
const startMemory = process.memoryUsage();
console.log(`Job started - Memory: ${Math.round(startMemory.heapUsed / 1024 / 1024)}MB`);
await performDataProcessing();
const endMemory = process.memoryUsage();
console.log(`Job completed - Memory: ${Math.round(endMemory.heapUsed / 1024 / 1024)}MB`);
});
```
#### Environment Variables
Access your application's environment variables within cron jobs:
```javascript
javascriptcron.schedule('0 */6 * * *', async () => {
const apiKey = process.env.EXTERNAL_API_KEY;
const environment = process.env.NODE_ENV;
if (environment === 'production') {
await syncProductionData(apiKey);
}
});
```
#### Logging Integration
Leverage Sherpa.sh's logging infrastructure for cron job monitoring:
```javascript
javascriptcron.schedule('0 3 * * *', async () => {
try {
console.log('[CRON] Starting backup process');
await performBackup();
console.log('[CRON] Backup completed successfully');
} catch (error) {
console.error('[CRON] Backup failed:', error.message);
// Logs are automatically captured by Sherpa.sh monitoring
}
});
```
### Basic Cron Implementation
Any standard cron library works well within this architecture:
#### Node.js Example
```javascript
const cron = require('node-cron');
// Daily backup at 3 AM
cron.schedule('0 3 * * *', async () => {
await performBackup();
});
// Hourly health check
cron.schedule('0 * * * *', async () => {
await healthCheck();
});
```
#### Python Example
#### Python Code for Scheduling Weekly Reports
The following Python code snippet utilizes `APScheduler` to schedule a weekly report generation every Monday at 9 AM. The job is handled in a background scheduler, which is gracefully shut down at exit.
```python
from apscheduler.schedulers.background import BackgroundScheduler
import atexit
# Create a background scheduler instance
scheduler = BackgroundScheduler()
# Schedule a weekly report generation
scheduler.add_job(
func=generate_weekly_report,
trigger="cron",
day_of_week='mon',
hour=9
)
# Start the scheduler
scheduler.start()
# Ensure scheduler shuts down cleanly at exit
atexit.register(lambda: scheduler.shutdown())
```
#### Key Points:
* **`BackgroundScheduler`**: Runs jobs in the background thread, making it suitable for web applications.
* **Cron Trigger**: Configured to execute the job every Monday at 9 AM.
* **Graceful Shutdown**: Uses `atexit` to register a shutdown command ensuring clean teardown of the scheduler.
### Enhanced Visibility with Schedo.dev
For production applications requiring better observability, monitoring, and reliability, we recommend **Schedo.dev** - a distributed cron job platform designed for modern development teams.
#### Why Schedo.dev?
**Built-in Reliability**: Automatic retries, error tracking, and comprehensive failure handling eliminate common cron job pitfalls.
**Zero Infrastructure Management**: No DevOps setup required - focus on business logic while Schedo handles scaling, concurrency, and infrastructure.
**Complete Observability**: Real-time execution logs, performance metrics, and failure alerts provide full visibility into job execution.
**Distributed Execution**: Built-in distributed locking ensures jobs run exactly once across your entire infrastructure, preventing race conditions.
**Developer Experience**: Local development support with the same API as production, plus seamless environment management.
#### Schedo.dev Integration
```javascript
const { schedo } = require('@schedo/sdk');
// Define scheduled job
schedo.defineJob(
'send-weekly-report', // Job identifier
'0 9 * * 1', // Schedule (Monday 9 AM)
async (ctx) => { // Handler function
await sendWeeklyReport(ctx.userId);
return 'Report sent successfully';
}
);
// Advanced job with retry configuration
schedo.defineJob(
'data-sync',
'*/15 * * * *', // Every 15 minutes
async (ctx) => {
await syncExternalData();
},
{
retries: 3,
timeout: '5m',
onFailure: async (error, ctx) => {
await notifyTeam(`Data sync failed: ${error.message}`);
}
}
);
```
#### When to Choose Schedo.dev
**Recommended for**:
* Production applications with critical scheduled tasks
* Teams needing detailed job monitoring and alerting
* Applications requiring distributed job execution
* Projects where job reliability is essential
**Basic cron is sufficient for**:
* Development and testing environments
* Simple, non-critical background tasks
* Applications with minimal observability requirements
### Best Practices
#### Error Handling
```javascript
const cron = require('node-cron');
cron.schedule('0 2 * * *', async () => {
try {
await performDailyMaintenance();
console.log('Daily maintenance completed successfully');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Daily maintenance failed:', error);
// Send alert to monitoring system
await sendAlert('Daily maintenance failure', error);
}
});
```
#### Logging and Monitoring
```javascript
const winston = require('winston');
const cron = require('node-cron');
const logger = winston.createLogger({
level: 'info',
format: winston.format.json(),
transports: [
new winston.transports.File({ filename: 'cron.log' })
]
});
cron.schedule('0 1 * * *', async () => {
logger.info('Starting nightly cleanup job');
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
await cleanupOldData();
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
logger.info(`Cleanup completed in ${duration}ms`);
} catch (error) {
logger.error('Cleanup failed', { error: error.message });
}
});
```
#### Resource Management
```javascript
// Schedule job to run every 6 hours
cron.schedule('0 */6 * * *', async () => {
try {
// Fetch data in manageable chunks
const batches = await getDataBatches();
for (const batch of batches) {
await processBatch(batch);
// Yield execution to allow garbage collection
await new Promise(resolve => setImmediate(resolve));
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error processing batches:', error);
}
});
```
### Environment Configuration
Configure different schedules for different environments:
```javascript
const schedules = {
development: '*/5 * * * *', // Every 5 minutes for testing
staging: '0 */2 * * *', // Every 2 hours
production: '0 2 * * *' // Daily at 2 AM
};
const environment = process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development';
const schedule = schedules[environment];
cron.schedule(schedule, async () => {
await performScheduledTask();
});
```
### Troubleshooting
#### Common Issues
**Jobs not executing**: Verify cron syntax and ensure the container process stays alive.
**Memory leaks**: Monitor memory usage in long-running jobs and implement proper cleanup.
**Timezone issues**: Explicitly set timezone in cron configuration or use UTC consistently.
To schedule a timezone-aware daily task in JavaScript using `node-cron`, you can use the following code:
```javascript
const cron = require('node-cron');
const nodemailer = require('nodemailer'); // Example: email sending function
// Define the function to be executed
async function sendDailyReport() {
// Your logic here
console.log("Daily report sent!");
}
// Schedule a task to run every day at 9 AM New York time
cron.schedule('0 9 * * *', async () => {
await sendDailyReport();
}, {
timezone: "America/New_York"
});
```
#### Debugging
Here's the updated JavaScript code with comprehensive logging:
```javascript
// Add comprehensive logging for debugging
cron.schedule('0 * * * *', async () => {
const startTime = new Date();
console.log(`Job started at ${startTime.toISOString()}`);
try {
const result = await performTask();
console.log('Job completed successfully:', {
result,
startTime: startTime.toISOString(),
endTime: new Date().toISOString(),
duration: `${new Date() - startTime}ms`
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Job failed:', {
error: error.message,
stack: error.stack,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
```
### Next Steps
* Implement basic cron jobs for your immediate needs
* Consider Schedo.dev for production applications requiring enhanced reliability
* Set up proper monitoring and alerting for critical scheduled tasks
* Review and optimize job performance regularly
# v0.3.0 - 9/04/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
March 21, 2025
# v0.3.0 - 9/04/25
This releases improves the domain management and adds customer requested functionality.
## New Features
* Ability to routing the Apex domain to the applicaiton for auto routed domains. If you wanted example.com to route to your application, that is now possible, where as before you could only route with a subdomain like www.example.com
* Framework detector: When new projects are imported we intelligently detect the framework and set the default build settings for the chosen framework.
## Improvements
* Improved Domain Management: The user experience now guides the creatino of new domains for both manually routed and
* Added the ability for "click to copy" to manual DNS records.
* Added "click to copy" for values in logs
## Bug Fixes
* Manual Cert Validations expire after 30 days if the CNAME is not made in time. Generate a new cert validation when this happens.
* CNAME Validation had race conditions when determining proper domain validation. This has been patched
* Ipv6 addresses didn't fit in the log column. Truncated and added to expandable details.
# v0.2.0 - 27/03/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
March 21, 2025
# v0.2.0 - 27/03/25
This releases adds support for popular AI generation tools like Loveable and Bolt. As well as additional frameworks and general improvements to the platform.
## New Features
* React Support: Now all frontend only react based projects can be deployed with sherpa.sh
* Lovable.app and Bolt.new support: All apps built using these AI tools can now be deployed on sherpa.sh.
## Improvements
* Gitbub App Improvements: If you haven't used sherpa.sh in a while you would have to reconnect your github app. We've added functionality to keep your connection fresh so you won't have to reconnect after long periods of inactivity
* Logging page: Better support for IPv6 and multiple frameworks.
## Bug Fixes
* Deployment errors with non nextjs react projects. See New feature: react support
# v0.3.1 - 22/4/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.3.1 - 22/4/25
## Bug Fixes
* Fixed bug in configuration wizard with selecting Docker container and not being able to save the form due to empty nextjs fields
* CNAME Record lookup validation errors happening sporadically for manual routed domains. Use multiple DNS servers to account for delayed propogation.
# v0.3.2 - 4/5/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.3.2 - 4/5/25
## Improvements
* Moved route domain routing out of the custom domain section to make it easier to read
* Adding an FAQ to the billing page in the portal to clear up questions around overages.
* We Added [additional packages](/applications/debugging#build-process-missing-a-dependency) to the base build alpine linux container. This means node-gyp is supported which is required by Payload CMS.
## Bug Fixes
* Manual Cert Validations expire after 30 days if the CNAME is not made in time. Generate a new cert validation when this happens.
* CNAME Validation had race conditions when determining proper domain validation. This has been patched
* Ipv6 addresses didn't fit in the log column. Truncated and added to expandable details.
# v0.4.1 - 9/6/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.4.1 - 9/6/25
## Release Notes - June 2025
This release focuses on infrastructure improvements, deployment reliability, and framework support enhancements. We've made significant progress on zero-downtime deployments and resolved several critical issues affecting build processes.
### Infrastructure Improvements
* **Zero-downtime deployments**: Reordered hostname and container management to eliminate downtime during deployments
* **Enhanced cache management**: Improved cache purging timing to prevent early purges that could affect site availability
* **CDN optimization**: Disabled CDN for Docker builds to improve deployment reliability
* **Better error handling**: Improved Kubernetes error conflict parsing for clearer deployment diagnostics
### Framework Support
* **SvelteKit enhancements**: Fixed static asset handling, hash generation, and service worker configuration
* **SvelteKit build optimization**: Resolved build order issues and improved overall stability
* **Remix integration**: Successfully integrated Remix framework support
* **PayloadCMS compatibility**: Fixed upload functionality bugs
* **Next.js improvements**: Resolved import timing issues and configuration warnings
### Deployment & Hosting
* **Branch subdomain fixes**: Corrected subdomain generation for branch deployments
* **Storage zone naming**: Fixed issues with storage zone names containing slashes from branch names
* **Domain management**: Improved domain handling and fixed bad domain detection
* **Ingress configuration**: Enhanced ingress setup for non-production branches
### User Experience
* **Build notifications**: Enhanced Discord messages for build success/failure with better domain information
* **Configuration handling**: Added support for frozen configuration files
* **DockerIgnore management**: Automatic removal of preset DockerIgnore files that could interfere with builds
### Bug Fixes
* Fixed hostnaming function that was causing deployment issues
* Resolved link deletion problems that caused downtime between builds
* Corrected pull zone configuration errors
* Fixed GitHub repository table display issues
* Addressed Bunny CDN integration problems
* Resolved import timing issues for various frameworks
* Fixed configuration account handling for frozen configs
# v0.4.0 - 22/5/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.4.0 - 22/5/25
This releases adds support for a variety of new features and frameworks as well as UX improvements
## New Features
* Official [Sveltekit](/supported-frameworks/sveltekit) support. We now detect and deploy the Sveltekit projects using the node-adapter and framework best practices.
* We've updated the backend so that all URLs for static assets are served from the same url as the main application instead of a different subdomain prefixed with `static-` .
* Added a `Purge Cache` button to the deployments and logs page for user control over CDN purging.
## Improvements
* If you have 1 team we automatically redirect you to the home page and skip the teams screen
* Envvariable input have auto complete turned off
* Streamlined onboarding process by removing verfication and long onboarding form.
* Added root domain routing instructions for manually routed domains to the domains settings section of projects.
## Bug Fixes
* If you had .dockerignore file that ignored the .next or .next/standalone build directories app deployment would fail. This has been patched - we now ignore the .dockerignore file since we are using a Sherpa.sh internal Dockerfile to build the project.
* Github integration was only showing the 30 most recent repos for import. We've updated this so it now shows all repos on the linked account/team.
* Some users experienced SSL cert issues due to a TypeError bug, this has been patched
* Fixed bug where couldn't choose between production and preview environments on log page
# v0.4.2 - 23/6/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.4.2 - 23/6/25
### New Features
* **Environment Management System**: New GUI for creating and managing deployment environments with Git push-to-deploy functionality. This allows users to put different envrionment variables for deployments of different branches.
* **Nuxt.js Support**: Added full Nuxt.js framework support with Docker and Jenkins CI/CD integration
* **New Onboarding Flow**: Redesigned user onboarding with 50for10 credit system
### Enhancements
* **Deployment**: Enhanced deployment table, improved manifest handling, and better environment variable management
* **CDN**: Cache bypass for redirects and retry mechanism for API reliability
* **UI**: Fixed z-index issues, improved popovers, and updated nameserver card
* **Stability**: Better container health checks and resolved Sharp image processing conflicts
### Bug Fixes
* Fixed Svelte node adapter and PayloadCMS cache handler issues
* Resolved multiple Dockerfile and Jenkins configuration problems
* Improved deployment pipeline reliability and error handling
* Cleaned up unnecessary logging and enhanced Git operations
# v0.4.3 - 27/6/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.4.3 - 27/6/25
### Framework Configuration Enhancements
#### **Configuration Management Improvements**
* **Unified Config Append System**: Implemented consistent configuration appending across all supported frameworks instead of importing configs, improving build reliability and modularity
* **Framework-Specific Updates**:
* **Next.js**: Enhanced config setup with proper append functionality and build optimizations
* **Nuxt.js**: Updated to support mixed ESM/CommonJS syntax and version 2.18+ compatibility
* **Remix**: Fixed configuration handling and improved move operations
* **Svelte**: Migrated to appended configuration system
* **TypeScript Support**: Extended configuration appending to work seamlessly with TypeScript projects
### Build System Optimizations
#### **Performance Improvements**
* **Asset Management**: Removed legacy public assets to significantly reduce build times
* **Node.js Support**: Dropped Node 16 support and improved ESM/CommonJS detection and handling
* **Environment Variables**: Enhanced environment variable handling during build processes, including support for empty variables
#### **Development Environment**
* **Marketing Site Cleanup**: Completely removed marketing site components and headers to streamline the codebase
* **Build Reliability**: Fixed various build issues across Next.js, Remix, and other frameworks
### Infrastructure & Operations
#### **Environment Management**
* **Build-Time Environment Variables**: Implemented proper environment variable injection during build processes
* **Configuration Validation**: Added better handling for null projects and improved icon display logic
#### **Logging & Monitoring**
* **Enhanced Logging**: Improved logging for rules processing and deployment operations
* **Root Domain Handling**: Fixed bugs related to root domain processing
* **Link Management**: Improved unlinking and relinking processes with better error handling
### Bug Fixes
#### **Configuration Issues**
* Fixed Nuxt configuration handling for projects with mixed module syntax
* Resolved Next.js build configuration problems
* Corrected Remix framework integration issues
#### **Build Pipeline**
* Fixed environment variable availability during build time
* Resolved TypeScript compatibility issues with configuration appending
* Improved error handling for empty or missing environment variables
#### **User Interface**
* Fixed icon display issues when project data is null
* Enhanced messaging for clear operations
* Improved overall user experience consistency
***
**Migration Notes**: Projects using older configuration import patterns will automatically benefit from the new append system. No manual intervention required for existing deployments.
# v0.5.0 - 9/7/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.5.0 - 9/7/25
## New Features
#### Singapore Region Support
* Added Singapore as a new deployment region with beta availability
* Expanded infrastructure to support Asia-Pacific deployments
#### Static Build Mode
* Introduced static site generation capabilities for improved performance
* Automated asset bundling and optimization for static deployments
* Bulk upload functionality for faster static asset deployment (10x speed improvement)
#### Dedicated Build Servers
* New dedicated compute options for build processes
* Isolated build environments for enhanced security and performance
* Configurable resource allocation for build workloads
## Enhancements
#### Framework Support
* Improved Nuxt.js deployment with better route handling and edge rules
* Enhanced support for Remix and Svelte frameworks
* Added framework-specific build optimizations
#### Performance Improvements
* Optimized memory allocation with new allocatable memory features
* Improved upload handling for Svelte and Remix applications
* Enhanced edge rule processing for faster content delivery
#### Developer Experience
* Simplified onboarding flow for users in multiple teams
* Better handling of environment variables including multiline JSON support
* Removed git settings from project wizard for streamlined setup
## Bug Fixes
#### Framework-Specific Fixes
* Fixed Nuxt v2 routing issues
#### Build Process
* Resolved Docker file path detection for non-turbo repositories
#### Configuration Issues
* Resolved ingress overlap conflicts
* Corrected environment variable escaping for proper newline support
# v0.5.1 - 29/7/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.5.1 - 29/7/25
### New Features
* **Next.js Subdirectory Support** - Projects using Next.js within subdirectories of Git repositories are now properly detected and deployed, making it easier to manage monorepo structures with multiple applications
* **Enhanced Branch Selection** - The branch selection interface now displays all available branches, giving you complete visibility into your repository's branch structure when setting up deployments
### Improvements
* **Nuxt.js Build Optimization** - Improved Nuxt.js build strategy with proper NITRO\_PRESET handling across all build commands, ensuring consistent deployment configurations regardless of your build setup
* **DNS Management Cleanup** - Removed unnecessary static URL references from the DNS configuration page, providing a cleaner and more focused domain management experience
* **Ingress Configuration Enhancement** - Increased header and cookie size limits in ingress configuration to prevent truncation issues with larger authentication tokens or session data
* **Domain Name Consistency** - All domain names are now automatically converted to lowercase, preventing case-sensitivity issues that could cause deployment failures
* **Dependabot Branch Filtering** - Automated dependency update branches are now excluded from automatic deployments, preventing unnecessary builds from dependency PRs
### Bug Fixes
* **Canonical Link Headers** - Corrected canonical URL generation to use proper hostnames instead of load balancer IP addresses, improving SEO and preventing redirect loops
* **Nuxt v2 Routing** - Fixed routing issues specific to Nuxt.js version 2 applications that were causing navigation problems
# v0.6.0 - 12/08/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v0.6.0 - 12/08/25
## New Features
**GitHub Account Management**
* Connect multiple GitHub accounts to your team for enhanced repository access
* Seamlessly switch between different GitHub accounts when importing projects
**Usage Analytics & Metrics**
* Track deployment usage with detailed metrics and visualizations
* Monitor bandwidth consumption through integrated metrics
* View historical usage data with monthly summaries
* Real-time progress bars for compute utilization
**Billing & Tier Management**
* New Pro tier (formerly Starter) with 100-500 deployments per month
* Simplified billing page with consolidated usage information
* Clear upgrade paths between Free and Pro tiers
* Deployment limits enforcement based on your subscription tier
## Improvements
**Enhanced Deployment Experience**
* Better error messaging for failed deployments. Including messaging during container builds, deployments, and file uploads
* Increased Helm deployment timeout to 120 seconds for complex applications
* Clearer output messages during container build process
**SSL & Security**
* Improved certificate management for custom domains
**User Experience**
* Streamlined sidebar navigation
* Better timezone handling for usage metrics (UTC standardization)
* Enhanced environment variable validation with clearer error messages
#### Bug Fixes
**Authentication & Access**
* Fixed redirect issues when connecting GitHub accounts with existing tokens
* Resolved problems with multiple team creation during onboarding
* Corrected access restrictions for free tier users importing multiple projects
**Logging & Monitoring**
* Fixed log filtering by environment
* Resolved issues with log fetching reliability
**UI & Navigation**
* Fixed click issues on the upgrade page
* Resolved billing usage alert display problems
# v1.0.0 - 11/09/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v1.0.0 - 11/09/25
We're thrilled to announce Version 1.0 - a complete reimagining of web deployment that makes shipping applications faster, simpler, and more reliable than ever before.
#### What's New
**More Intelligent Framework Detection** Our platform now automatically detects your framework and configures optimal build settings. No more manual configuration - we analyze your project and handle everything from build commands to output directories.
**Clean URL Architecture** We've eliminated versioned hashes from your URLs. Your applications now use the same clean paths in production that you see in development:
* Before: `yourapp.com/a7f3b2/_next/static/...`
* After: `yourapp.com/_next/static/...`
This means better SEO, consistent analytics, and familiar debugging paths.
**Fewer Build Failures & Easier Debigging** Our new build system prevents errors before they happen with:
* 4GB default memory allocation
* Framework-specific optimization strategies
* Real-time validation and helpful error messages
* Automatic dependency resolution
**Monorepo-First Design** Select any package from your monorepo and deploy it with a single click. We automatically handle workspace dependencies, shared packages, and build orchestration.
:::caution
**Note:** We've temporarily deprecated support for PayloadCMS and Nuxt2 while we complete our infrastructure migration. React projects have been ported to Vite projects. If your react project's build process does not use Vite, you may need to customize your configuration. Reach out on [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh) for help.
:::
**New Features**
**Monorepo Support**
* Full support for Turborepo, Nx and other monorepo project structures and builders
* Automatic detection and configuration for monorepo deployments
* Project selection interface for choosing specific packages within monorepos
* Improved handling of workspace dependencies and build paths
**Framework Detection & Strategy System**
* Automatic framework detection using more comprehensive detection algorithms. That will automatically extract install and build commands.
* New deployment strategy for Static Vite projects
* Support for both static and server-side rendering configurations on all supported fraemworks.
* Docker deployment support with customizable Dockerfile uploads
**Environment Variables Management**
* New YAML-based environment variable configuration
* JSON object storage for complex environment configurations
* Dotenvx integration for secure environment variable handling
**Improvements**
**Build System Enhancements**
* Increased default build memory to 4GB for complex applications
* Better error messaging during build failures and file uploads
* Improved build output directory detection
**Framework-Specific Optimizations**
* Next.js standalone builds with proper static/SSR handling
* SvelteKit support for both static and Node adapters
* Remix deployment with Vite compiler integration
* Nuxt3 deployment configuration improvements
**SSL & Domain Management**
* Extended SSL certificate expiration to 90 days
* Improved edge rule management for static vs dynamic content
* Better handling of custom subdomain configurations
* Fixed A Record option display in domain linking
**Bug Fixes**
**Deployment Issues**
* Fixed deployment update attempts when deployments don't exist
* Resolved Vite build configuration issues
* Fixed environment variables being erased on save when a searchable parameters is present.
**Framework Detection**
* Fixed issues with major version detection for frameworks
**Environment Configuration**
* Fixed NODE\_ENV handling in build processes
* Corrected environment variable parsing in deployment workflows to account for apostraphes and special characters
**UI & Navigation**
* Fixed form submission issues with switch components
* Resolved build settings page error display
* Corrected wizard default values for environment variables
* Fixed unique subdomain validation on environment copy
# v1.1.0 - 10/07/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v1.1.0 - 10/07/25
This release focuses on improving performance, monorepo support, and framework compatibility with several important bug fixes.
#### What's New
**Smart Caching System** We've enabled intelligent caching that dramatically improves deployment speeds by reusing build artifacts when possible. The system automatically detects when dependencies haven't changed and skips unnecessary rebuilds.
**Enhanced Monorepo Experience** We've improved the monorepo workflow with better package selection, clearer dependency resolution, and more intuitive project navigation.
**Vite 7 Support** Full compatibility with Vite 7, ensuring you can use the latest build tools with all their performance improvements.
**Astro Support** We've added full support for Astro, the modern web framework for building content-rich websites. Deploy your Astro projects with automatic detection and optimized build configurations.
**New Features**
**Performance & Caching**
* Smart caching system for faster deployments
* Optimized cache population and validation
* Improved handling of stale cache entries
**Monorepo Enhancements**
* Better monorepo project selection and navigation
* Improved workspace dependency resolution
* Enhanced support for empty git repositories
**Improvements**
**Framework Support**
* Astro framework support with automatic detection and configuration
* Vite 7 compatibility
* Better framework detection for invalid semver versions
* Improved Next.js Dockerfile configuration
* Enhanced dotenvx integration for Next.js projects
**Build System**
* Removed inaccurate timing from log steps for cleaner output
* Better static file copying for Next.js deployments
* Optimized output directory handling
**Pricing & UI**
* Updated pricing structure
* Improved delete confirmation text
* Fixed buggy header on login page
**Bug Fixes**
**Framework-Specific Issues**
* Fixed Dockerfile configuration for Next.js static builds
* Resolved Remix deployment bugs
* Corrected edge rules for Next.js image optimization
* Fixed dotenvx environment variable handling in Next.js
**Build & Deployment**
* Fixed framework detection with invalid semver versions
* Resolved cache-related deployment issues
* Fixed handling of empty git repositories during deployment
* Corrected static file copying for Next.js
**UI & Configuration**
* Fixed JSON parse error for environment data on frontend
* Resolved undefined settingsResponse.settings error
* Fixed buggy header display on login page (#22)
* Corrected Sentry error tracking integration
# v1.2.0 - 10/14/25
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# v1.2.0 - 10/14/25
This release introduces two major security and reliability features that make migrating to Sherpa.sh safer and protecting your applications easier than ever.
#### What's New
**SafetyNet - Zero-Risk Migration** We've launched [SafetyNet](/infrastructure/safety-net), our zero-risk migration feature that lets you deploy on Sherpa.sh while keeping your existing provider (Vercel, Netlify, AWS, etc.) as an automatic fallback. Start saving money immediately without the risk of moving everything to a new platform. If Sherpa.sh ever returns an error, traffic automatically fails over to your configured fallback provider without any manual intervention or DNS changes.
**Web Application Firewall (WAF)** We've added comprehensive [WAF protection](/infrastructure/web-application-firewall-waf) to automatically protect your applications from common vulnerabilities and sophisticated attacks. The firewall inspects incoming HTTP requests in real-time, filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches your application - with zero configuration required.
**New Features**
**SafetyNet Migration & Disaster Recovery**
* Automatic fallback routing to your existing provider when Sherpa.sh returns errors
* Intelligent edge routing powered by 200+ global CDN locations
* Request preservation including headers, body, authentication, and cookies
* Sub-second automatic failover with 50-150ms latency impact
* Works with all frameworks and application types
* CDN caching of fallback responses for cost optimization
* Real-time monitoring of fallback usage and traffic distribution
* One-click testing by temporarily disabling your application
**Web Application Firewall (WAF)**
* Automatic protection against OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities
* Real-time blocking of SQL injection, XSS, and RCE attacks
* Protection against 400+ known attack patterns and CVEs
* Machine learning-based threat detection with continuous updates
* Zero-day exploit protection
* Malicious bot traffic filtering
* Web shell detection and blocking
* Real-time security monitoring and blocked request visibility
* Geographic threat mapping
* 100% free protection - just message support to enable
**Improvements**
**Security & Reliability**
* Enhanced protection against injection attacks (SQL, NoSQL, Command, LDAP)
* Comprehensive XSS protection (Reflected, Stored, DOM-based)
* Protocol attack prevention (HTTP smuggling, header injection, parameter pollution)
* File inclusion attack blocking (LFI, RFI, path traversal)
* Framework-specific vulnerability protection (PHP, Java, Node.js, Ruby, Perl)
* Data leakage prevention across multiple databases and platforms
**Edge Infrastructure**
* V8 isolate runtime for fast edge script execution with sub-millisecond startup
* Proximity-based execution across global CDN network
* Framework-agnostic edge routing supporting all Sherpa.sh frameworks
* Intelligent caching for fallback responses
**Migration Experience**
* Immediate cost savings with gradual migration support
* Zero downtime risk during platform transitions
* Visual verification tools for testing SafetyNet activation
* Comprehensive request logging for fallback monitoring
# MongoDB
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# MongoDB
Coming soon. We are currently working on a managed MongoDB offering. It should be live in the near future.
# MySQL
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# MySQL
Coming soon. We are currently working on a managed Mysql offering. It should be live in the near future.
# App Configuration
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# App Configuration
The sherpa.sh platform supports many different types of frameworks using the same simple settings. Below are the most common settings you need to set to deploy your web app.
## Default Domain
This is the domain where you're application will be reachable by your users. It is fully customizable.
By default, your web app will be assigned a subdomain under `sherpa.software`. This is the address where users can access your application. For example, if your app is named "myapp," it will default to `myapp.sherpa.software`.
You can always change this domain to suit your preferences, or use a [custom domain](/getting-started/custom-domains).
## Build Settings
There are different build settings depending on what type of app you are building:
* [View Javascript Build Settings](#javascript-applications)
* [View Docker Build Settings](#docker-settings)
### Javascript Applications
The commands that are run when building the production version of your app. Typically, these are the install and build commands in your `package.json`file.
You can use the following support package managers:
* npm
* pnpm
* yarn
* bun
Need something else? [Let us know](https://sherpa.sh/contact).
### Framework
Select your projects framework. When your app is deployed we use your framework's best practices to optimize the infrastructure for your application. This means we setup all the appropriate cache-headers, distributed caching, and scaling algorithms to ensure a fast, delightful, and personalized customer experience.
If the framework you need is not listed or supported, [let us know](https://sherp.sh/contact), we'll add it faster than you think!
### Install Command
How you install your node modules and packages. Typically this is a command from your `package.json.` For example: `npm i`.
:::tip
Your project is installed into a Linux container with a litany of standard binaries. \
[Learn more about our container runtime](/applications/runtime-environment).
:::
### Build Command
How you build your project. Like `npm run build`. We set `NODE_ENV=production` by default for all builds of javascript applications. You can override this with [environment variables](#environment-variables).
:::note
**Supporting .mjs files:** Your project must support .mjs file types. If you have this disabled via eslint or typescript rules, you will need to enable it for your builds to complete.
If you are unsure, you likely do not need to worry about this. Most modern JS frameworks enforce this by default.
:::
### Output Directory
The path where your build command outputs the built files **Usually you want to leave this as the default value**.
If you run into trouble, open a chat with us and we'll be happy to help you get setup.
:::note
If your app folder is nested in a repo subfolder, you want to use the [root directory](#root-directory) setting to set that folder, not the output directory.
:::
### Static Generation Only
When this is toggled on, Sherpa.sh will build and deploy your project using SSG (Static Site Generation). You must ensure that your project is configured appropriately, and the correct output directory is set for your deployment.
:::caution
Some frameworks require you to explicitly set the build process for SSG in your codebase. For example, in Next.js projects you must have `output: export` set in your `next.config.ts/js` . Not doing so could result in failed deployments or unexpected behavior.
:::
## Docker Applications
#### Docker Settings
Two different settings are essential for Docker applications:
* **Dockerfile**: The name of the Dockerfile to build your application. If your docker file is not named `Dockerfile` this is where you put that value.
* **Port**: The port that your application exposes. Set the value of the exposed port that the application listens to in the container. This can only be one port. If you have multiple services that run on different ports please put them in separate containers. If they are in the same repo, you can import the repository twice and set different Dockerfile settings.
## Root Directory
Sometimes your application will be in a sub-directory of your repo. Set this value to the directory path of your application in your repo. For example if you have a NextJS app inside of your repo in the path `root > projects > mynextapp` , in the _root directory_ setting you would put the value `projects/mynextapp`.
All [Build Setting](#build-settings) commands will run inside this folder.
## Environment Variables
Environment variables are key-value pairs accessible via `process.env` in your Node.js application, both during build and runtime.
### Processing Conventions
Our platform processes environment variables through a specific pipeline:
1. **Adding Variables**: Environment variables added in the gui (including pasting `.env` files) are parsed into JSON using [dotenv](https://github.com/motdotla/dotenv) and saved securely in the Sherpa.sh infrastructure.
2. **Building Process Access to Variables**: At build time, variables are written to a file in your build directory called `.env.local` and loaded into the bash environment along with any other `.env` files in your repo via [dotenvx](https://github.com/dotenvx/dotenvx) (See [resolution order](#resolution-order) below for variables resolution with multiple .env files). Additionally, `NODE_ENV` defaults to `production` unless explicitly set.
3. **Application Access to Variables**: At deployment time, the environment variables JSON is converted to YAML via [js-yaml](https://github.com/nodeca/js-yaml) and injected into the Docker container environment. These env variables are available in the OS for your backend application. Additionally, the `.env.local` file written during the build process will ensure all environment variables are available in the `process.env` of your application (based on your frameworks conventions for injecting variables into `process.env` these will be avaiable in both the frontend and backend)
:::caution
Be cautious with the variables you expose to your application’s frontend. Framework-specific prefixes expose variables to client-side code:
* Next.js: `NEXT_PUBLIC_*`
* Vite: `VITE_*`
* Create React App: `REACT_APP_*`
Never expose API keys, database credentials, or secrets through these prefixes. Always ensure sensitive data remains secure and is not included in these public-facing variables. Please refer to your framework's documentation for more info.
:::
### Resolution Order
#### Standard Projects (Non-Next.js)
Following [dotenv-flow conventions](https://github.com/kerimdzhanov/dotenv-flow), files are loaded in priority order:
1. `.env.{NODE_ENV}.local` (e.g., `.env.production.local`)
2. `.env.local` (ignored when `NODE_ENV=test`) _**\***__**Added by Sherpa.sh with your env vars.**_
3. `.env.{NODE_ENV}` (e.g., `.env.production`)
4. `.env`
#### Next.js Projects
Following [Next.js conventions](https://nextjs.org/docs/pages/building-your-application/configuring/environment-variables#environment-variable-load-order):
1. `process.env`
2. `.env.$(NODE_ENV).local`
3. `.env.local` (not loaded when `NODE_ENV=test`) _**\***__**Added by Sherpa.sh with your env vars.**_
4. `.env.$(NODE_ENV)`
5. `.env`
### Formatting
:::note
**Note**: Because your app will be deployed with Docker, environment variable keys that are valid in `.env` files may be stripped when saved to ensure Docker/Kubernetes compatibility. See [Valid Keys](#valid-keys) Below.
:::
#### Special Characters
Based on [dotenv](https://github.com/motdotla/dotenv) parsing behavior, here's how special characters are interpreted and made available to `process.env`:
Character/Pattern
Input
process.env output
Notes
Newlines
"Line1\nLine2"
Line1\nLine2
\n becomes actual newline
Escaped newlines
"Line1\\nLine2"
Line1\\nLine2
\\n preserved as literal
Carriage returns
"Line1\r\nLine2"
Line1\r\nLine2
Windows line endings preserved
Quotes in values
"This is \"quoted\""
This is \"quoted\"
Escape sequences preserved
Dollar signs
'$HOME won't expand'
$HOME won't expand
Single quotes prevent expansion
Backslashes
"C:\path\to\file"
C:\path\to\file
Single backslash preserved
Double backslashes
"C:\\path"
C:\\path
Literal backslashes
Special escapes
"\t \r \n"
Tab, CR, LF characters
Escape sequences interpreted
Multiline actual
"Line1
Line2"
Line1\nLine2
Actual line breaks become \n
Comments
value # comment
value
Comments stripped
Leading/trailing spaces
` value `
value
Spaces trimmed unless quoted
#### Valid Keys
Environment variables must be compatible with Kubernetes naming conventions since they're deployed to Docker containers. Keys are validated against the pattern: `[-._a-zA-Z][-._a-zA-Z0-9]*`
**Filtered Keys** (automatically removed):
* Starting with numbers: `123KEY`, `1_VARIABLE`
* Containing spaces: `MY KEY`, `VARIABLE NAME`
* Special characters: `KEY@EMAIL`, `KEY#HASH`, `KEY$DOLLAR`, `KEY-WITH-DASH`
* Dots in names: `KEY.WITH.DOT`, `app.config.value`
**Valid Keys**:
* Alphanumeric with underscores: `API_KEY`, `DATABASE_URL`, `PORT_3000`
* Starting with letters: `MY_VAR`, `abc123`
* Starting with underscore: `_PRIVATE`, `__INTERNAL__`
* Mixed case: `MyVariable`, `camelCase`
:::tip
**Securing Credentials:** We follow security best-practices for securing your environment variables. Environment variables are stored on a secure server. Access is controlled with extremely limited RBAC. Credentials are only gathered on a as-needed basis to build your project. Otherwise they are always stored securely at rest.
This approach ensures that no unauthorized sherpa.sh employees can view your secrets.
:::
## App Region
When configuring your app region, you can choose from three options:
* US East (N. Virginia),
* US West (N. California)
* EU Central (Frankfurt, Germany).
This selection determines where your application will run. You want to select the location closest to your database(s) to minimize latency to and from your data.
For more information, see our [regions documentation](/getting-started/regions).
:::note
Depending on your project's setup, many requests will hit your content cached on our global CDN and not your application - for example with partial pre-renders, cached content will exist on the network edge and your application will do minimal work to service the request.
For further info on the architecture, please refer to our [architecture](/infrastructure/architecture) documentation.
:::
## NodeJS Version
The version of Node to use for the build process and for running your application.
## Branch Settings
Configure how [continuous delivery](/applications/continuous-delivery) works on your application.
The selected branch will be the production branch, meaning any new commit on that branch will trigger a build and deployment to your [Default Domain](#default-domain).
A build and deployment to a preview environment will also be triggered when a new pull request is opened for a different branch. New commits on branches with open pull requests will also trigger a new build and deployment to a preview environment. You can disable automatic deployments of preview branches by disabling _auto branch deployments._
# Postgres
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Postgres
Coming soon. We are currently working on a managed Postgres offering. It should be live in the near future.
# Custom Domains
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Custom Domains
This guide walks you through adding and configuring custom domains for your Sherpa.sh projects. You can choose between automated DNS management or manual record configuration.
## Overview
Sherpa.sh supports unlimited custom domains on any paid plan. You have two configuration options:
* **Automated (Recommended)**: Point your nameservers to Sherpa.sh for automatic DNS management
* **Manual**: Maintain your DNS provider and add specific records per project
## Prerequisites
* Paid plan on Sherpa.sh
* Domain registered with a DNS provider
* Access to your domain's DNS settings
## Adding a Custom Domain
1. Navigate to the **Domains** tab in your Sherpa.sh dashboard
2. Click **Add New Domain**
3. Enter your domain name (e.g., `example.com`)
4. Click **Save**
### Method 1: Automated DNS Management (Recommended)
This method provides the most seamless experience with automatic SSL certificate generation and CDN optimization.
#### **Step 1: Update Nameservers**
After adding your domain, navigate to the DNS Management section:
1. Go to your domain's settings page
2. Note the Sherpa.sh nameservers:
* `ns1.sherpa.sh`
* `ns2.sherpa.sh`
3. Update your domain registrar's nameservers to point to Sherpa.sh
:::caution
**Important**: Some providers (like GoDaddy) don't support CNAME-based nameserver forwarding. For these providers, use the direct Bunny.net nameservers (our underlying DNS provider):
* `kiki.bunny.net`
* `coco.bunny.net`
Alternatively, you can use the IP addresses directly:\
* `91.200.176.1`
* `109.104.147.1`
:::
#### **Step 2: Link Domain to Application**
1. Navigate to your domain in the Sherpa.sh dashboard
2. Click **Link Application**
3. Select your target application from the dropdown
4. Click **Save**
### Method 2: Manual DNS Configuration
Use this method if you prefer to manage DNS through your existing provider.
#### **Step 1: Link Domain to Application**
Follow the same steps as automated method to link your domain to an application.
#### **Step 2: Add Required DNS Records**
Navigate to your application's page's domain settings to view [required records](#required-dns-records) and add them in your DNS provider
### Manual DNS Configuration: Required Records
When managing DNS through your existing provider, you'll need to configure specific records to route traffic to Sherpa.sh infrastructure. Here's exactly what each record does and important considerations for root domain routing.
#### Understanding the Record Structure
Each DNS record serves a specific purpose in the routing chain:
* **Application routing**: Directs user traffic to your application
* **SSL validation**: Proves domain ownership for certificate generation
* **Static assets**: Optimizes delivery of images, CSS, and JavaScript files
#### Required DNS Records by Domain Type
#### **Subdomain Configuration (Recommended)**
For subdomains like `www.example.com` or `app.example.com`:
```
Type: CNAME
Name: www (or your chosen subdomain)
Value: example.sherpa.softwareTTL: 3600
```
**What this does**: Routes all traffic for your subdomain through Sherpa.sh's CDN network, providing optimal performance and automatic scaling.
**Static assets optimization**:
```
Type: CNAME
Name: static-www (or static-[yoursubdomain])
Value: static-example.sherpa.softwareTTL: 3600
```
:::tip
This is a legacy record left over from previous architectures, it will soon be removed from the dashboard. It is required for now, but will be removed in the future. When we remove it, you will not have to do anything on your side, everything will continue working as expected.
:::
#### **Root Domain Configuration**
If you want to use your root domain as your main url, root domains (like `example.com`) have DNS limitations that require special handling:
Root domain configuration is required when this switch is enabled
**Option 1 - ALIAS/ANAME Record** (Best Performance):
:::danger
It is **strongly** recommend that you use Option 1. If your provider does not support Option 1 it is better to use a subdomain `www.example.com` instead of `example.com` as the main url of your website.
:::
```
Type: ALIAS (or ANAME/FLATTENING depending on provider)
Name: @ (or leave blank)
Value: sherpa.sherpa.softwareTTL: 3600
```
**Supported providers**: Cloudflare, AWS Route53, DNSimple, Namecheap, and more\
**Benefits**: Full CDN support, optimal performance, proper SSL handling
:::note
#### Why CNAMEs Don't Work on Root Domains
CNAME records cannot be placed at the root domain level because DNS standards dictate that the root domain must not have CNAME records due to the way DNS queries are resolved. A CNAME at the root would conflict with other essential DNS records like MX records.
#### How Some Providers Support Root Domain CNAMEs
Some DNS providers use proprietary solutions like ALIAS, ANAME, or CNAME flattening to overcome this limitation. These custom records allow the root domain to redirect traffic similarly to a CNAME while maintaining compatibility with the DNS protocol. This ensures seamless integration with services that require domain aliases without breaking DNS rules. But not all providers support this functionality.
:::
**Option 2 - A Record** (Compatibility Fallback):
```
Type: A
Name: @ (or leave blank)
Value: [Load balancer IP]
TTL: 3600
```
**When to use**: Only when your DNS provider doesn't support ALIAS/ANAME records \
**Limitations**:
* Bypasses CDN, resulting in slower global performance
* Direct server connection increases bandwidth usage
* No automatic failover if IP changes
* May impact your billing due to increased origin bandwidth consumption
#### **Performance Impact Comparison**
**Subdomain with CNAME** (Optimal):
* Request path: User → CDN Edge → Origin Server
* Benefits: Caching, compression, DDoS protection
* Latency: 20-50ms globally
**Root domain with A record** (Suboptimal):
* Request path: User → Origin Server (direct)
* Limitations: No caching, higher latency, increased bandwidth
* Latency: 100-300ms depending on user location
#### SSL Certificate Validation Record
Required for all configurations to enable HTTPS:
```
Type: CNAME
Name: _acme-challenge
Value: _acme-challenge.example.com.validation.sherpa.software
TTL: 300
```
**Important**: This record is used by Let's Encrypt to verify domain ownership. Keep it even after SSL activation for automatic renewals.
## Debugging DNS Routing
If you are having issues setting up your custome domain's DNS routing. Please follow the following steps:
### 1. Check DNS propagation
If you are using our [Automated DNS Management (method 1)](#method-1-automated-dns-management-recommended) your domain won't be available until propagation is completed. To check propagation you can use [https://www.whatsmydns.net/#NS/](https://www.whatsmydns.net/#NS/) and search for your domain's NS server propogation. Once your nameservers are fully propogated, redeploy the application that your've linked your custom domain to.
If you are using [Manual Managment (method 2)](#method-2-manual-dns-configuration) your domain won't be available until propagation is completed. You can use [https://www.whatsmydns.net/#CNAME/](https://www.whatsmydns.net/#CNAME/) to check the CNAME propagation of all the required fields on the domains page of your application.
### 2. Redeploy application
Once propogation is complete, redepooy your application to have it pick up the new DNS routing changes. If you deploy before propogation is completed your custom domain, SSL cert, or other routing may not work.
### 3. Open a Support Ticket
If you still have trouble, visit [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh) and open a ticket in the `#support` channel with your account email, application, and domain information.
## Domain Configuration Options
Once linked, configure these settings on your domain's page:
#### Root Domain Routing
* **Route root domain to this project**: Directs `example.com` to your application. Requires [root domain configuration](#root-domain-configuration).
* **Redirect root domain to subdomain**: Redirects `example.com` → `www.example.com`
#### Best Practices
1. **Use Subdomains**: We recommend using `www` or another subdomain as your primary domain rather than the root domain for better CDN compatibility
2. **Root Domain Limitations**:
* Some DNS providers don't support CNAME records on root domains
* Using A records bypasses CDN benefits, potentially increasing origin bandwidth usage
3. **SSL Certificates**: Keep the `_acme-challenge` record even after SSL generation for future renewals
### Verification and Troubleshooting
#### Check DNS Propagation
After updating records:
1. Click **Refresh** in the domain settings
2. Check status indicators (✓ = configured correctly)
3. Allow 5-48 hours for full DNS propagation
#### Common Issues
**Nameserver Conflicts:**
* Ensure no conflicting records exist at your DNS provider
* Remove any existing A/CNAME records for configured subdomains
**SSL Certificate Errors:**
* Verify `_acme-challenge` record is correctly configured
* Check for typos in the validation record value
**CDN Bypass Warning:**
* If using A records for root domain, traffic bypasses CDN
* Consider upgrading your plan if hitting bandwidth limits
### Support
Need assistance? Join our Discord community: [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh)
####
# Getting Started
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Getting Started
The faster you can get your code to production, the faster you can satisfy your users. With sherpa.sh it is easy to go from local development to production. You can get started with any pre-existing Github repo. All you need to do is [create a free account](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up), connect your Github Repo, and choose a domain name. Two minutes later, your app is online across the world!
## Step 1: Sign-up for a free account
Head over to the sherpa.sh website and [create a free account](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up).
## Step 2: Link your Github
:::note
The sherpa.sh platform helps you iterate faster. You get continuous delivery by default when connecting a Github Repo. This means new commits to your repository are automatically deployed.
[Learn more about continuous delivery.](#continuous-deployment)
:::
Login to your account and click "Applications". Here you will be prompted to connect your Github account.
Click the Connect Github Button
When prompted, grant the Sherpa.sh app permission to the repo you want to deploy. Alternatively, grant access to all repos to deploy multiple applications.
The repos your granted Sherpa.sh access to will appear in the table. Select the repo you wish to deploy.
## Step 3: Configure & Deploy
Your repo will be linked and you will be prompted to [configure your application](/getting-started/configuration). Fill out all the appropriate fields (Pro tip: you probably don't have to fill out any of them! We detect your framework for you.)
Once you are satisfied with your configuration click _Save and Deploy_.
And that's it! Your app will be queued for building and deployment. Build logs will be available on the deployment page. You will receive a notification in a few minutes when your app is live!
# Regions
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
Global Deployment Infrastructure
# Regions
### Deploy Around the Globe
Enhance your app's performance by deploying to data centers around the world. Experience reduced latency and improved speed for all your users through our worldwide coverage of compute regions and content delivery network.
### Compute Regions
Deploy your app close to your database and users in one of our four compute data centers strategically positioned around the world:
| Region | Location | Data Center Code |
| ------------ | ---------------------- | ---------------- |
| eu-central | Frankfurt, Germany | fsn1 |
| us-east | Ashburn, Virginia, USA | ash |
| us-west | Hillsboro, Oregon, USA | hil |
| ap-southeast | Singapore | sin |
**Note:** Singapore region (`ap-southeast`) coming soon. [Contact us](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact) for more information.
Our global infrastructure is powered by **Hetzner**, providing reliable and high-performance hosting for your applications.
### Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Accelerate the delivery of static content to your users by leveraging our globally distributed CDN servers, strategically located in over 119 cities across more than 100 countries worldwide.
Our Global CDN is powered by **Bunny CDN**, ensuring fast content delivery with minimal latency.
#### CDN Locations
**Europe**
* Amsterdam
* Athens
* Belgrade
* Bratislava
* Brussels
* Budapest
* Bucharest
* Chisinau
* Copenhagen
* Dublin
* Frankfurt **Volume**
* Frankfurt
* Helsinki
* Keflavik
* Kyiv
* Lisbon
* Ljubljana
* London
* Luxembourg
* Madrid
* Marseille
* Milan
* Moscow
* Novi Travnik
* Nicosia
* Oslo
* Paris **Volume**
* Prague
* Riga
* Sofia
* Stockholm
* Vienna
* Vilnius
* Warsaw
* Zagreb
* Zurich
**North America**
* Ashburn
* Atlanta
* Boston
* Charlotte
* Chicago **Volume**
* Dallas **Volume**
* Denver
* Honolulu
* Houston
* Kansas City
* Los Angeles **Volume**
* Miami **Volume**
* Minneapolis
* Montreal
* New York
* Ogden
* Phoenix
* Pittsburgh
* San Jose
* Seattle
* Toronto
* Vancouver
**Latin America (LATAM)**
* Brasilia
* Bogota
* Buenos Aires
* Curitiba
* Fortaleza
* Guatemala
* La Paz
* Lima
* Mexico City
* Porto Alegre
* Quito
* Rio de Janeiro
* Salvador
* San Juan
* San Pedro
* Santiago
* Sao Paulo **Volume**
* Sao Paulo
**Asia**
* Almaty
* Baku
* Bangkok
* Bangalore
* Chennai
* Dhaka
* Hong Kong **Volume**
* Ho Chi Minh
* Istanbul
* Jakarta
* Karachi
* Kathmandu
* Kolkata
* Kuala Lumpur
* Manila
* Mumbai
* New Delhi
* Phnom Penh
* Seoul
* Singapore **Volume**
* Singapore
* Taipei
* Tbilisi
* Tel Aviv
* Tokyo **Volume**
* Ulaanbaatar
* Yangon
* Yerevan
**Oceania**
* Adelaide
* Auckland
* Brisbane
* Hagatna
* Melbourne
* Perth
* Sydney
**Middle East & Africa**
* Baghdad **ISP**
* Bahrain
* Cairo **ISP**
* Cape Town
* Dubai
* Fujairah
* Johannesburg
* Lagos
* Luanda
* Nairobi
* Riyadh
**Volume** locations indicate high-capacity edge servers for handling larger traffic loads.\
**ISP** locations indicate servers hosted within internet service provider networks.
### Choosing the Right Region
When deploying your application, consider the following factors for selecting a compute region:
* Location of your database and other infrastructure components. You want to minimize roundtrip latency from your applicaiton to your other infrastructure.
* Geographic location of your primary user base
* Regional compliance and data residency requirements
* Need for redundancy across multiple regions
By default, all CDN locations are enabled on each deployment.
For guidance on selecting the optimal deployment configuration for your specific needs, please contact our support team.
# Application Servers
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Application Servers
Your application's backend code and Docker containers run on sherpa.sh's application servers. These servers sit behind our CDN and load balancer within our Kubernetes cluster in your selected region, providing a robust execution environment for your applications.
### How It Works
When you deploy your application, sherpa.sh runs your backend code or Docker containers on our application servers. These servers handle all the compute-intensive work while our CDN and load balancer manage traffic distribution and static content delivery.
**Architecture Flow**:
1. **User request** → CDN (static files) or Load Balancer (dynamic content)
2. **Load Balancer** → Application Server instances
3. **Application Servers** → Your backend code/containers
4. **Response** flows back through the same path
For detailed architecture information, see our [Architecture Overview](/infrastructure/architecture) page.
### Default Resource Configuration
Every application server gets deployed as a swarm of docker containers behind a loadbalancer. There is a maximum resource allocation per individual container.
#### Resource Allocation
```yaml
# Per instance limits
CPU: 1 core maximum
Memory: 1GB maximum
```
#### Auto-scaling Behavior
The amount of replicas of your containers that get created depends on your plan selected.
```yaml
# Hobby and Starter Plan Settings
Minimum instances: 1
Maximum instances: 5
CPU scaling threshold: 80%
```
**How scaling works**: When your backend code uses more than 80% CPU across instances, new application servers automatically spin up to handle the load.
If you need more instance replicas or different CPU thresholdes, reach out to support in [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh).
### Infrastructure Types
#### Shared Application Servers (Default)
**What you get**: Your containers/code run on shared infrastructure alongside other applications.
**Benefits**:
* **Zero configuration**: Deploy immediately
* **Automatic load distribution**: Traffic spreads across instances
* **Cost-effective**: Shared infrastructure costs
* **Built-in monitoring**: Performance metrics included
**Limitations**:
* **Ephemeral storage**: No persistent file writes
* **Shared resources**: CPU/memory shared with other applications
* **Standard resource limits**: Fixed allocation per instance
**Best for**: Stateless APIs, web applications, microservices
#### Dedicated Application Servers
**What you get**: Exclusive physical servers running only your application containers.
**Available Configurations**:
* **Compute**: 2-96 CPU cores, 4-256GB memory
* **Storage**: 80GB-300TB persistent disk
* **Network**: 1-10Gbps dedicated bandwidth
* **Transfer**: 20TB monthly included
**Benefits**:
* **Guaranteed performance**: No resource contention
* **Persistent storage**: File system writes supported
* **Custom sizing**: Tailored to your workload
* **Isolation**: Enhanced security and performance
**Best for**: Databases, file processing, high-traffic applications
### Regional Deployment
Your application servers run in the region you select during deployment. View our [available regions](/getting-started/regions).
**Benefits of regional deployment**:
* **Reduced latency**: Servers closer to your users
* **Data compliance**: Meet regional data requirements
* **Improved performance**: Faster database connections
### Managing Application Servers
#### Viewing Server Status
1. Navigate to your application dashboard
2. Go to **Resources > Application Server**
3. Monitor instance count, CPU usage, and memory consumption
#### Requesting Dedicated Servers
1. Visit [discord.sherpa.sh](https://discord.sherpa.sh)
2. Create support ticket with requirements:
* Expected traffic volume
* Resource requirements (CPU/memory)
* Storage needs
* Performance requirements
### Best Practices
#### Stateless Design
Design your application to work seamlessly across multiple server instances by avoiding in-memory state storage.
**Good: External State Management**
```javascript
// pages/api/users/[id].js
import { getUser } from '../../../lib/database';
export default async function handler(req, res) {
const { id } = req.query;
// Fetch from external database, not server memory
const user = await getUser(id);
if (!user) {
return res.status(404).json({ error: 'User not found' });
}
res.status(200).json(user);
}
```
**Avoid: In-Memory State**
```javascript
// Don't do this - data lost during scaling
let userCache = {}; // Lost when new instances start
export default async function handler(req, res) {
const { id } = req.query;
if (!userCache[id]) {
userCache[id] = await getUser(id); // Won't persist across instances
}
res.status(200).json(userCache[id]);
}
```
#### Health Check Implementation
Sherpa.sh automatically checks your application health by requesting the root URL (`/`). Ensure this endpoint returns a valid response.
**Required Health Check Setup**
```javascript
// pages/index.js or app/page.js (App Router)
export default function Home() {
return (
Application Status: Healthy
Server is running normally
);
}
// Or for API-only applications
// pages/index.js
export default function handler(req, res) {
res.status(200).json({
status: 'healthy',
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
version: process.env.npm_package_version || '1.0.0'
});
}
```
**Advanced Health Check with Dependencies**
```javascript
// pages/index.js
import { checkDatabase } from '../lib/database';
import { checkExternalAPI } from '../lib/external-services';
export default async function handler(req, res) {
try {
// Check critical dependencies
await checkDatabase();
await checkExternalAPI();
res.status(200).json({
status: 'healthy',
checks: {
database: 'connected',
external_api: 'responding'
},
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
} catch (error) {
res.status(503).json({
status: 'unhealthy',
error: error.message,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
}
}
```
#### Efficient Resource Usage
Optimize your application for auto-scaling by implementing efficient async patterns and resource management.
**Database Connection Management**
```javascript
// lib/database.js
import { Pool } from 'pg';
// Use connection pooling for database efficiency
const pool = new Pool({
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL,
max: 20, // Maximum connections
idleTimeoutMillis: 30000,
connectionTimeoutMillis: 2000,
});
export async function queryDatabase(query, params) {
const client = await pool.connect();
try {
const result = await client.query(query, params);
return result.rows;
} finally {
client.release(); // Always release connection
}
}
```
**Async API Route Optimization**
```javascript
// pages/api/products/search.js
export default async function handler(req, res) {
const { query, category } = req.query;
try {
// Run parallel requests for better performance
const [products, categories, recommendations] = await Promise.all([
searchProducts(query),
getCategories(category),
getRecommendations(query)
]);
res.status(200).json({
products,
categories,
recommendations
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Search error:', error);
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Search failed' });
}
}
```
### Monitoring and Optimization
#### Performance Metrics
* **CPU utilization**: Monitor for scaling triggers
* **Memory usage**: Track memory leaks and optimization opportunities
* **Response time**: Measure application performance
* **Instance count**: Understand scaling patterns
#### Optimization Strategies
* **Database optimization**: Use connection pooling and query optimization
* **Caching**: Implement Redis or in-memory caching
* **Async processing**: Use background tasks for heavy operations
* **Resource monitoring**: Set up alerts for resource usage
### Next Steps
* **Review architecture**: Read our Architecture Overview for complete system understanding
* **Set up monitoring**: Configure application performance monitoring
* **Implement caching**: Add Redis or similar caching layer
* **Plan scaling**: Consider dedicated servers for growing applications
* **Optimize performance**: Profile your application for bottlenecks
Need help optimizing your application server setup? Our [support team](https://discord.sherpa.sh) provides detailed performance analysis and recommendations for your specific use case.
# Architecture Overview
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Architecture Overview
Our infrastructure follows a modern distributed architecture pattern that prioritizes scalability, reliability, and performance. We know some developers don't like magic. So we've done our best to be transparent about how our underlying infrastructure is put together. If you have questions, feel free to [reach out](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact).
## The Big Picture
Think of our infrastructure as a well-oiled assembly line (but for you application, not cars). Each component has a specific job, and they work together to deliver top performance for your application:
* **CDN (Content Delivery Network)**: Global servers that cache your static assets, as well as pages and parts of your web application. The CDN is configured to listen to your webframeworks specific `cache-control` headers and other caching related quirks (like `stale-while-revalidate`). [Read more about our optimized CDN setup](/infrastructure/cdn-and-caching) and how it's different than competitors.
* **Kubernetes**: All functions in your applications are containerized then managed and scaled by one of our many Kubernetes clusters. As request volume increases, our system automatically scales up your application behind one of our many load balancers. This ensures smooth handling of traffic spikes while maintaining consistent performance. The containerized nature of the deployment means your application runs in identical environments across all instances, eliminating environment-related issues. Each cluster consists of a minimum of 3 redundant control planes as well as multiple compute nodes that autoscale up in seconds when resource thresholds are met. This ensures there is always slack capacity for applications that have hard traffic spikes.
* **Global Cache**: Our system's short-term memory, storing frequently accessed data for ISR, PPR, and other framework based caching functionality. You framework leverages this cache to fulfill requests faster and improve page load speeds.
* **Build Servers**: Everytime you push to github and trigger a deployment your code changes are picked up by our build servers. These servers build, package, and ship your application code to the appropriate CDN, k8s cluster, and caching servers.
## How It All Connects
Requests flow through our system like this:
```mermaid
Request
--> CDN (checks closest server first)
--> CDN Cache Hit
--> Response
--> CDN Cache Miss
--> K8s App Server (app may call global cache) (multiple containers are load balanced)
--> Response
GitHub Push
--> Build Process (all in the CD Servers)
--> Global Cache Creation
--> CDN Upload & Configuration
--> K8s Deployment
```
This setup ensures we maintain high availability while keeping response times snappy. Each component will get its own deep-dive page, but this overview should give you the 30,000-foot view of how everything fits together.
# CDN & Caching
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# CDN & Caching
Sherpa.sh provides high-performance content delivery and caching through our global CDN infrastructure, powered by bunny.net's industry-leading network. Our CDN automatically optimizes content delivery for your applications while providing flexible caching controls for different deployment scenarios.
## Performance Advantages on Sherpa.sh
#### Global Network Infrastructure
Our CDN delivers industry-leading performance with:
* **200+ Points of Presence (PoPs)** strategically located worldwide
* **25.45ms average global latency** - significantly lower than competitors
* **95% cache hit ratio** ensuring optimal content delivery
* **100Gbit uplinks** with NVMe storage at major PoPs
#### Regional Performance Comparison
Sherpa.sh CDN consistently outperforms legacy CDN providers across all major regions:
* **North America**: 15-20ms average latency
* **Europe**: 18-25ms average latency
* **Asia-Pacific**: 22-28ms average latency
* **Latin America**: 25-35ms average latency
* **Africa**: 30-45ms average latency
## How Our Caching Works
### Framework-Aware Caching
When deploying full-stack frameworks, Sherpa.sh intelligently listens to your framework's default cache-control headers and configures caching settings accordingly. We optimize these settings based on established best practices for each framework.
**Next.js Example:**
Below you will find and example of how our framework aware caching performs on a nextjs app. This intelligent caching occurs for all our supported frameworks
### Static Assets
* **Path**: `/_next/static/*`
* **Cache-Control**: `public, max-age=31536000, immutable`
* **Purpose**: Cached for 1 year to improve performance.
### API Routes
* **Path**: `/api/*`
* **Cache-Control**: `no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate`
* **Purpose**: Not cached by default to ensure data is always fresh.
### Server-side Rendered Pages
* **Cache-Control**: `public, max-age=0, must-revalidate`
* **Purpose**: Short cache life with revalidation to update content dynamically.
### Static Pages
* **Cache-Control**: `public, max-age=3600, stale-while-revalidate=86400`
* **Purpose**: Cached with background updates to allow fresh content while ensuring availability.
Our system automatically recognizes these patterns and applies optimal caching strategies:
* **Static assets**: Long-term caching with immutable flag
* **API endpoints**: Bypassed from CDN cache
* **Dynamic pages**: Smart caching with background refresh
* **Image optimization**: Automatic format conversion and caching
## Default Caching Behavior
By default Sherpa.sh always respects the Cache-Control and Expire headers returned by the application. If no headers are present, no caching in the CDN will occur. Most frameworks (like nextjs, will automatically return the appropriate headers for you) while some others (like Sveltekit) require you to explicitly return them.
Below is a list of extensions that are cachable for fullstack frameworks:
#### List of cacheable extensions:
| 3g2 | 3gp | 7z | ai | asf | avi | avif | apk |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ----- | --- | ---- | --- |
| bin | bat | bmp | bz2 | class | css | csv | dat |
| doc | docx | dll | dmg | ejs | eot | eps | exe |
| flac | flv | heic | gif | gz | ico | iso | jar |
| jpg | jpeg | js | m3u8 | m4u | mid | midi | mkv |
| mp3 | mp4 | mpa | mpg | odt | ogg | otf | pdf |
| pict | pls | png | ppt | pptx | ps | psd | rar |
| srt | svg | svg2 | swf | tar | tif | tiff | ttf |
| vob | webm | webp | woff | woff2 | wav | wma | xls |
| xlsx | zip | zst | ts | txt | yuv | | |
#### MIME types that will not be cached:
| text/html | application/json | application/xml | |
| --------- | ---------------- | --------------- | - |
## Default caching behavior of static builds
If you have enabled [static site generation in your build settings](/getting-started/configuration#static-generation-only), Sherpa.sh will default to caching everything. You can control how long items are cached with the cache-control and expire headers.
## Global Key-Value Store
Sherpa.sh includes a global KV store that serves as the backend cache for various frameworks. This is separate from our CDN caching layer and provides:
* **Low-latency data access** across all deployment regions
* **Automatic replication** for high availability
* **Framework integration** for session storage, API caching, and more
* **Edge computing support** for serverless functions
Note: This KV store is distinct from CDN caching and focuses on application-level data storage.
## Docker Deployment Caching
### Manual Cache Header Configuration
When deploying Docker containers, you must set cache-control headers manually since containerized applications don't have framework-specific defaults.
**Setting Cache Headers in Docker Applications:**
```dockerfile
# Example: Node.js Express application
FROM node:18-alpine
COPY . .
RUN npm install
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "server.js"]
```
```javascript
// server.js - Manual header configuration
app.use(
'/static',
express.static('public', {
maxAge: '1y',
etag: false,
lastModified: false
})
);
app.get('/api/*', (req, res) => {
res.set('Cache-Control', 'no-store');
// API logic here
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=3600, stale-while-revalidate=86400');
res.send('Hello World');
```
#### Cache-Control Headers Reference
Understanding when and how to use different cache-control directives is crucial for optimal performance. Here's a comprehensive guide:
#### Cache-Control Policy Guidelines
**1. Static Assets (CSS, JS, Images with Versioning):**
* `Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable`
**2. HTML Pages with Dynamic Content:**
* `Cache-Control: public, max-age=3600, stale-while-revalidate=86400`
**3. API Responses That Change Frequently:**
* `Cache-Control: public, max-age=300, must-revalidate`
**4. Sensitive or User-Specific Content:**
* `Cache-Control: private, max-age=0, no-cache`
**5. Content That Should Never Be Cached:**
* \`Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must
**Key Directives Explained:**
* `public`: Cacheable by CDN and browsers
* `private`: Only cacheable by browsers
* `max-age`: Cache lifetime in seconds
* `stale-while-revalidate`: Serve stale content while updating
* `immutable`: Content never changes (perfect for versioned assets)
* `no-store`: Never cache anywhere
For detailed information about HTTP caching headers, refer to the [MDN Cache-Control documentation](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cache-Control).
## CDN Configuration Options
#### Automatic CDN Deployment
Sherpa.sh automatically places a CDN in front of every deployment by default. This provides:
* **Global content distribution** across 200+ edge locations
* **Automatic SSL termination** and certificate management
* **DDoS protection** and security filtering
* **Image optimization** and format conversion
#### Docker CDN Recommendations
For Docker deployments, you can disable CDN if needed, though this is typically recommended only when:
* You're unsure whether your framework sets appropriate cache-control headers
* Your application requires direct server connections
* You're implementing custom caching logic
**Best Practice**: Keep CDN enabled and configure proper cache headers instead of disabling CDN entirely.
## Advanced Caching Features
Sherpa.sh automatically implements sophisticated caching optimizations behind the scenes to maximize performance and reliability. Here's what happens under the hood when your application is deployed.
### Smart Cache Intelligence
#### Automatic File Type Detection
When your application serves content, our CDN automatically analyzes each request and determines the optimal caching strategy:
**What happens internally:**
* File extensions and MIME types are analyzed in real-time
* Static assets (CSS, JS, images) receive aggressive caching
* Dynamic endpoints are intelligently bypassed
* Binary files are optimized for streaming delivery
#### Query String Normalization
Our system automatically sorts query parameters to improve cache hit rates:
```http
# These requests are treated as identical:
GET /api/resize?width=200&height=100&format=webp
GET /api/resize?format=webp&height=100&width=200
GET /api/resize?height=100&width=200&format=webp
# Result: Single cached response serves all three requests
```
**Benefits for developers:**
* Higher cache hit rates without code changes
* Reduced origin server load
* Consistent response times regardless of parameter order
### Intelligent Cache Variations
#### Browser Capability Detection
The CDN automatically detects browser capabilities and serves optimized content:
# Modern browser request:
# Accept: image/avif,image/webp,image/*
# Serves: optimized AVIF format (90% smaller) Cache-Key: image.jpg:avif-support
# Legacy browser request:
# Accept: image/*
# Serves: standard JPEG format Cache-Key: image.jpg:no-avif-support
#### Device-Aware Caching
Content is automatically optimized based on device characteristics:
```http
# Mobile device:User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS...) # Serves: Mobile-optimized images and CSS
# Desktop device:User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS...) # Serves: High-resolution desktop assets
```
#### Geographic Optimization
Content delivery is optimized based on user location:
```http
# User in Europe:
# Serves from Amsterdam PoP (12ms latency)
# Includes region-specific optimizations
# User in Asia:
# Serves from Tokyo PoP (8ms latency)
# Applies Asia-Pacific performance tweaks
```
### Resilient Content Delivery
#### Error Response Protection
The CDN automatically protects your origin server from cascading failures:
```http
# Origin server returns 500 error
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
# CDN behavior:
1. Caches error response for 5 seconds
2. Serves cached error to subsequent requests
3. Prevents origin server overload during incidents
4. Automatically retries after cache expiration
```
#### Stale Content Serving
When your origin server is unreachable or updating, users still receive content:
```http
# Scenario 1: Origin server offline
Origin Status: Connection refused
CDN Response: Serves last known good version Cache-Control: stale-while-revalidate
# Scenario 2: Content being updated
Origin Status: Updating cache in background
CDN Response: Serves current cached version immediately
Update Status: New content ready for next request
```
**Real-world impact:**
* 99.9% uptime even during origin server issues
* Zero-downtime deployments
* Seamless user experience during maintenance
### Performance Optimizations
#### Video Content Handling
Large media files receive special treatment:
```http
# Video file request with byte range:
GET /video.mp4Range: bytes=1000000-2000000
# CDN behavior:
1. Splits file into 5MB chunks during first request
2. Caches chunks independently
3. Serves partial content without hitting origin
4. Enables video scrubbing for uncached content
```
#### Multi-Layer Caching
Your content benefits from multiple caching layers:
```
Request Flow:
Browser Cache (immediate)
↓ (cache miss)Edge PoP Cache (5-25ms)
↓ (cache miss) Regional Cache (25-50ms)
↓ (cache miss) Origin Server (50-200ms)
```
### Developer Benefits
#### Zero Configuration Required
All optimizations work automatically:
* No cache headers to configure for frameworks
* Automatic performance improvements
* Self-tuning based on traffic patterns
#### Built-in Best Practices
The system implements industry standards:
* Proper cache invalidation strategies
* Optimal TTL values for different content types
* Automatic security header injection
### Troubleshooting Common Scenarios
#### Low Cache Hit Rates
The system automatically adjusts when hit rates drop:
* Analyzes traffic patterns
* Adjusts cache TTL values
* Optimizes query string handling
#### Content Update Delays
Stale content serving ensures smooth updates:
* New content propagates in background
* Users never see loading states
* Automatic cache purging when needed
This intelligent caching layer operates transparently, requiring no configuration while delivering maximum performance benefits for your applications.
# Compliance
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Compliance
We prioritize building trust through transparency, rigorous standards, and partnerships with industry-leading infrastructure providers. Here's how we approach security and stability:
### Infrastructure Selection
We partner with established cloud infrastructure providers that:
* Maintain SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS certifications
* Undergo regular independent security audits and vulnerability assessments
* Implement continuous monitoring and proactive risk management
* Have proven track records in the industry, being in business for at least 10 years.
* Consistent operational stability with clear incident response protocols and transparency
### High Availability Architecture
Our infrastructure is designed with redundancy at every layer:
* Multi-node Kubernetes clusters distributed across multiple availability zones.
* At least three control planes per cluster to ensure continuous orchestration
* Multiple provider integration to eliminate single points of failure
* Replicated storage systems with automated failover capabilities
* Regular automated backups of all critical infrastructure components
* Designed for maximum uptime and rapid disaster recovery
### Our Security Journey
We are actively working with TrustCloud Security Assurance platform to evolve and monitor our security processes. This partnership helps us:
* Implement industry best practices
* Track our security posture
* Develop comprehensive security documentation
* Progress toward key compliance certifications such as SOC 2 Type II.
:::tip
**Note**: If you require SOC 2 Type II or other compliance certificates for your evaluation process, please [contact our team](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact). We are a bootstrapped company and are waiting for the right customer to ask before paying for compliance certificates. We have an auditor selected and waiting.
:::
# SafetyNet
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# SafetyNet
SafetyNet is the Sherpa.sh zero-risk migration feature that lets you deploy on our platform while keeping your existing provider (Vercel, Netlify, AWS, etc.) as an automatic fallback. Start saving money immediately without the risk of moving everything to a new platform.
Beyond migrations, SafetyNet also serves as a powerful disaster recovery solution. If your primary Sherpa.sh deployment ever experiences issues, traffic automatically fails over to your configured fallback provider without any manual intervention or DNS changes.
## How It Works
SafetyNet uses intelligent edge routing on our CDN to serve traffic from Sherpa.sh by default. If Sherpa.sh ever returns an error, your traffic automatically falls back to your existing deployment - instantly and transparently to your users.
```
User Request -> Sherpa.sh CDN Edge
|
V
[Sherpa.sh returns success]
|
V
Response served from Sherpa.sh
```
```
User Request -> Sherpa.sh CDN Edge
|
V
[Sherpa.sh returns error]
|
V
Automatic fallback to Vercel|Netlify|etc
|
V
Response served from Vercel|Netlify|etc
```
This approach means you can:
- **Start saving immediately** as Sherpa.sh handles your traffic at our flat rate
- **Reduce your Vercel bill** as usage drops
- **Keep your existing deployment** as a safety net
- **Zero downtime risk** during the transition
## Perfect For
SafetyNet is ideal if you are:
- Testing Sherpa.sh with production traffic before fully committing
- Gradually migrating from another platform without downtime risk
- Looking to reduce infrastructure costs immediately
- Wanting to keep your current provider as disaster recovery
## Configuration
Setting up SafetyNet is simple - just enable it from your application settings and configure your fallback URL.
### Prerequisites
- An active Sherpa.sh deployment
- Your existing deployment URL (e.g., `your-app.vercel.app`)
### Enabling SafetyNet
1. Navigate to **Applications > Your App > SafetyNet** in the Sherpa.sh dashboard
2. Enable SafetyNet for your application
3. Enter your fallback URL (e.g., `https://your-app.vercel.app`)
4. Save your configuration
That is it! SafetyNet is now active and will automatically route traffic to your fallback if Sherpa.sh returns an error.
### Testing SafetyNet
You can verify that SafetyNet is working correctly by temporarily disabling your Sherpa.sh application:
1. Navigate to your application settings page
2. Use the **toggle in the upper left** of the page to disable your application
3. Visit your domain - traffic should now be served from your fallback provider
4. Re-enable your application using the same toggle
5. Visit your domain again - traffic should now be served from Sherpa.sh
When you disable your application, it suspends on the backend, which causes SafetyNet to automatically activate and route all traffic to your configured fallback URL. This is a safe way to test the failover behavior without any actual errors or downtime.
#### Verifying the SafetyNet is Active
You can confirm which provider is serving your traffic using these methods:
**Check Response Headers:**
Inspect the HTTP response headers in your browser's developer tools (Network tab). Look for provider-specific headers:
- **Vercel**: `x-vercel-id`, `x-vercel-cache`
- **Netlify**: `x-nf-request-id`, `x-netlify`
- **Other providers**: Check their documentation for identifying headers
**Deploy a Visual Change:**
A foolproof way to test:
1. Make a visible change to your application (e.g., add a banner saying "Served from Vercel")
2. Deploy this change only to your fallback provider (not to Sherpa.sh)
3. Disable your Sherpa.sh application using the toggle
4. Visit your domain - you should see the change you deployed to the fallback
5. Re-enable Sherpa.sh - the change should disappear as traffic returns to Sherpa.sh
**Monitor Fallback Provider Logs:**
Check the access logs or analytics dashboard of your fallback provider (Vercel, Netlify, etc.) to see incoming requests when SafetyNet is active. This confirms traffic is reaching your fallback infrastructure.
:::note
**CDN Caching Saves You Money**
Even when SafetyNet routes to your fallback provider, responses with appropriate `cache-control` headers will be cached by our CDN. This means:
- Subsequent requests are served from our edge cache, not your fallback provider
- Your fallback provider sees dramatically reduced traffic and resource usage
- You save money on both providers while maintaining high performance
This intelligent caching ensures SafetyNet not only provides reliability but also cost efficiency.
:::
### How the Edge Script Works
Behind the scenes, SafetyNet uses an edge script that runs on our Bunny.net-powered CDN infrastructure:
```typescript
/**
* Intercepts origin responses and implements fallback logic
*/
async function onOriginResponse(context: {
request: Request,
response: Response
}): Promise | Response | void {
// If Sherpa.sh returns an error
if (!context.response.ok)) {
const originalUrl = new URL(context.request.url);
// Your fallback URL (Vercel, Netlify, etc.)
const fallbackHost = 'https://your-app.vercel.app';
const newUrl = `${fallbackHost}${originalUrl.pathname}${originalUrl.search}`;
// Forward the request to your fallback provider
const response = await fetch(newUrl, {
method: context.request.method,
headers: context.request.headers,
body: context.request.body,
redirect: context.request.redirect,
integrity: context.request.integrity,
signal: context.request.signal,
credentials: context.request.credentials,
mode: context.request.mode,
referrer: context.request.referrer,
referrerPolicy: context.request.referrerPolicy
});
return response;
}
}
```
## How Edge Scripting Works
SafetyNet leverages edge scripting technology to run code on our CDN, as close as possible to your users. Here is what makes it powerful:
### Proximity-Based Execution
Scripts run on CDN edge nodes across our global network, minimizing latency by executing closer to end users.
### V8 Isolate Runtime
Edge scripts run inside V8 isolates (the same engine powering Google Chrome), providing efficient and secure execution with fast startup times (sub-millisecond) and strong isolation between requests.
### Framework-Agnostic
SafetyNet works with any application [framework or technology stack supported by Sherpa.sh](/applications/supported-frameworks):
- Next.js, Remix, Nuxt, SvelteKit, etc
- Docker containers
- Static sites
- Custom applications
## What Triggers a Fallback
SafetyNet automatically routes to your fallback provider when:
- **4xx errors** (404, 403, etc.) - Client errors from your Sherpa.sh deployment
- **5xx errors** (500, 502, 503, etc.) - Server errors from your Sherpa.sh deployment
- **Connection timeouts** - If Sherpa.sh does not respond
- **Network errors** - Any network-level issues
Successful responses (2xx codes, 3xx) are always served from Sherpa.sh.
## Performance Characteristics
### Latency Impact
- **Normal operation**: No additional latency - traffic routes directly to Sherpa.sh
- **Fallback activation**: Adds 50-150ms for the intitial fallback request
- **Edge decision**: Sub-millisecond overhead for the routing logic
### Global Availability
SafetyNet runs across our [200+ global CDN edge locations](/infrastructure/cdn-and-caching), providing:
- Low-latency fallback decisions worldwide
- Regional optimization
- High availability routing
## Monitoring Your Migration
### Tracking Fallback Usage
You can monitor how often SafetyNet activates your fallback by reviewing:
- CDN access logs in your Sherpa.sh dashboard
- Response times and error rates
- Traffic distribution between Sherpa.sh and your fallback provider
### Gradual Cost Reduction
As your Sherpa.sh deployment handles more traffic successfully:
1. Your fallback provider sees decreasing usage
2. Your bills from the fallback provider decrease proportionally
3. You can monitor the cost savings in real-time
4. Once confident, you can remove the fallback entirely
## Disabling SafetyNet
Once you are confident in your Sherpa.sh deployment, you can disable the safety net in the same place you enabled it.
But there is no rush - keep SafetyNet active as long as you need it.
## Comparison with Standard Migration
| Approach | Risk Level | Cost Savings Start | Rollback Speed |
|----------|------------|-------------------|----------------|
| **SafetyNet** | Minimal | Immediate | Automatic (sub-second) |
| **Standard Migration** | Higher | After full switch | Manual (DNS propagation) |
## Technical Details
### Request Preservation
SafetyNet preserves all aspects of the original request when falling back:
- HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- All request headers (authentication, cookies, user-agent, etc.)
- Request body (for POST/PUT requests)
- Query parameters and search strings
- URL path
- Redirect behavior
- Request integrity
- Request signal
- Credentials
- CORS mode
- Referrer and referrer policy
This ensures your fallback provider receives identical requests, maintaining full compatibility with authentication, form submissions, API calls, and any other request-dependent functionality.
### Security Considerations
- Edge scripts run in isolated environments
- No access to sensitive data or credentials
- Cannot modify your Sherpa.sh or fallback deployments
- Audit logs available for compliance
## Frequently Asked Questions
**Does SafetyNet increase my costs?**
No. You only pay the Sherpa.sh flat rate. Your fallback provider bills decrease as Sherpa.sh handles more traffic.
**How fast is the fallback?**
Typically 50-150ms to reroute to your fallback provider. Users experience minimal delay.
**Can I use multiple fallback providers?**
Currently SafetyNet supports one fallback URL per deployment.
**Does this work with API routes?**
Yes. SafetyNet works for all HTTP requests, including API endpoints, static assets, and server-rendered pages.
**What if my fallback provider has issues?**
If both Sherpa.sh and your fallback fail, users see the error from the fallback provider. This is the same behavior as if you were only on the fallback provider.
**Can I customize which errors trigger fallback?**
The default configuration falls back on all error responses. Contact support for custom edge script configurations.
## Getting Started
Ready to try SafetyNet?
1. [Deploy your app to Sherpa.sh](/getting-started/quickstart)
2. Navigate to **Applications > Your App > SafetyNet**
3. Enable SafetyNet and enter your fallback URL
4. Start saving money immediately while your existing deployment remains as backup
Questions? Join us on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
# WAF (Web App Firewall)
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Protect your web applications and APIs from common vulnerabilities and sophisticated attacks with Sherpa.sh WAF. The firewall automatically inspects incoming HTTP requests in real-time, filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches your application.
### Overview
The Sherpa.sh WAF provides automatic protection against:
* SQL injection attacks
* Cross-site scripting (XSS)
* OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities
* Zero-day exploits
* Malicious bot traffic
No configuration required—just enable and you're protected.
### How It Works
The WAF uses machine learning and continuously updated threat intelligence to identify and block malicious requests automatically. When a request arrives:
1. **Request Analysis**: Every HTTP request is inspected against known attack patterns
2. **Threat Scoring**: Suspicious requests receive a threat score based on multiple factors
3. **Automatic Action**: High-risk requests are blocked instantly, while legitimate traffic flows through
4. **Continuous Learning**: The system adapts to new threats without manual updates
### Getting Started
#### Prerequisites
* Active Sherpa.sh account with deployed app
#### Enable WAF Protection
:::note
Message support in discord.sherpa.sh to have your WAF enabled. 100% Free.
:::
### Protection Features
#### Automatic Threat Detection
The WAF automatically protects against the following attacks
**Injection Attacks**
* SQL injection
* NoSQL injection
* Command injection
* LDAP injection
**Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)**
* Reflected XSS
* Stored XSS
* DOM-based XSS
**Security Misconfigurations**
* Exposed sensitive endpoints
* Directory traversal attempts
* File inclusion attacks
**Known Vulnerabilities**
* CVE-based exploits
* Framework-specific attacks
* CMS vulnerabilities
#### Real-Time Monitoring
View your application's security status at a glance:
* **Blocked Requests**: See threats stopped in real-time
* **Attack Patterns**: Identify trending attack types
* **Traffic Insights**: Understand normal vs suspicious behavior
* **Geographic Threats**: Map attack origins
### Full protection list
METHOD ENFORCEMENT
* 911100 - Method is not allowed by policy
SCANNER DETECTION
* 913100 - Found User-Agent associated with security scanner
MULTIPART ATTACK
* 922100 - Multipart content type global _charset_ definition is not allowed by policy
* 922110 - Illegal MIME Multipart Header content-type: charset parameter
* 922120 - Content-Transfer-Encoding was deprecated by rfc7578 in 2015 and should not be used
PROTOCOL ATTACK
* 921110 - HTTP Request Smuggling Attack
* 921120 - HTTP Response Splitting Attack
* 921130 - HTTP Response Splitting Attack
* 921140 - HTTP Header Injection Attack via headers
* 921150 - HTTP Header Injection Attack via payload (CR/LF detected)
* 921160 - HTTP Header Injection Attack via payload (CR/LF and header-name detected)
* 921190 - HTTP Splitting (CR/LF in request filename detected)
* 921200 - LDAP Injection Attack
* 921421 - Content-Type header: Dangerous content type outside the mime type declaration
* 921240 - mod\_proxy attack attempt detected
* 921151 - HTTP Header Injection Attack via payload (CR/LF detected)
* 921422 - Content-Type header: Dangerous content type outside the mime type declaration
* 921230 - HTTP Range Header detected
* 921180 - HTTP Parameter Pollution (%{TX.1})
* 921210 - HTTP Parameter Pollution after detecting bogus char after parameter array
* 921220 - HTTP Parameter Pollution possible via array notation
APPLICATION ATTACK LFI
* 930100 - Path Traversal Attack (/../) or (/.../)
* 930110 - Path Traversal Attack (/../) or (/.../)
* 930120 - OS File Access Attempt
* 930130 - Restricted File Access Attempt
* 930121 - OS File Access Attempt in REQUEST\_HEADERS
APPLICATION ATTACK RFI
* 931100 - Possible Remote File Inclusion (RFI) Attack: URL Parameter using IP Address
* 931110 - Possible Remote File Inclusion (RFI) Attack: Common RFI Vulnerable Parameter Name used w/URL Payload
* 931120 - Possible Remote File Inclusion (RFI) Attack: URL Payload Used w/Trailing Question Mark Character (?)
* 931130 - Possible Remote File Inclusion (RFI) Attack: Off-Domain Reference/Link
* 931131 - Possible Remote File Inclusion (RFI) Attack: Off-Domain Reference/Link
APPLICATION ATTACK RCE
* 932230 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection (2-3 chars)
* 932235 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection (command without evasion)
* 932120 - Remote Command Execution: Windows PowerShell Command Found
* 932125 - Remote Command Execution: Windows Powershell Alias Command Injection
* 932130 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Expression Found
* 932140 - Remote Command Execution: Windows FOR/IF Command Found
* 932250 - Remote Command Execution: Direct Unix Command Execution
* 932260 - Remote Command Execution: Direct Unix Command Execution
* 932330 - Remote Command Execution: Unix shell history invocation
* 932160 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found
* 932170 - Remote Command Execution: Shellshock (CVE-2014-6271)
* 932171 - Remote Command Execution: Shellshock (CVE-2014-6271)
* 932175 - Remote Command Execution: Unix shell alias invocation
* 932180 - Restricted File Upload Attempt
* 932370 - Remote Command Execution: Windows Command Injection
* 932380 - Remote Command Execution: Windows Command Injection
* 932231 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection
* 932131 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Expression Found
* 932200 - RCE Bypass Technique
* 932205 - RCE Bypass Technique
* 932206 - RCE Bypass Technique
* 932220 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection with pipe
* 932240 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection evasion attempt detected
* 932210 - Remote Command Execution: SQLite System Command Execution
* 932300 - Remote Command Execution: SMTP Command Execution
* 932310 - Remote Command Execution: IMAP Command Execution
* 932320 - Remote Command Execution: POP3 Command Execution
* 932236 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection (command without evasion)
* 932239 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection found in user-agent or referer header
* 932161 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found in REQUEST\_HEADERS
* 932232 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Command Injection
* 932237 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found in REQUEST\_HEADERS
* 932238 - Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found in REQUEST\_HEADERS
* 932190 - Remote Command Execution: Wildcard bypass technique attempt
* 932301 - Remote Command Execution: SMTP Command Execution
* 932311 - Remote Command Execution: IMAP Command Execution
* 932321 - Remote Command Execution: POP3 Command Execution
* 932331 - Remote Command Execution: Unix shell history invocation
PPLICATION ATTACK PHP
* 933100 - PHP Injection Attack: PHP Open Tag Found
* 933110 - PHP Injection Attack: PHP Script File Upload Found
* 933120 - PHP Injection Attack: Configuration Directive Found
* 933130 - PHP Injection Attack: Variables Found
* 933140 - PHP Injection Attack: I/O Stream Found
* 933200 - PHP Injection Attack: Wrapper scheme detected
* 933150 - PHP Injection Attack: High-Risk PHP Function Name Found
* 933160 - PHP Injection Attack: High-Risk PHP Function Call Found
* 933170 - PHP Injection Attack: Serialized Object Injection
* 933180 - PHP Injection Attack: Variable Function Call Found
* 933210 - PHP Injection Attack: Variable Function Call Found
* 933151 - PHP Injection Attack: Medium-Risk PHP Function Name Found
* 933131 - PHP Injection Attack: Variables Found
* 933161 - PHP Injection Attack: Low-Value PHP Function Call Found
* 933111 - PHP Injection Attack: PHP Script File Upload Found
* 933190 - PHP Injection Attack: PHP Closing Tag Found
* 933211 - PHP Injection Attack: Variable Function Call Found
APPLICATION ATTACK GENERIC
* 934100 - Node.js Injection Attack 1/2
* 934110 - Possible Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF) Attack: Cloud provider metadata URL in Parameter
* 934130 - JavaScript Prototype Pollution
* 934150 - Ruby Injection Attack
* 934160 - Node.js DoS attack
* 934170 - PHP data scheme attack
* 934101 - Node.js Injection Attack 2/2
* 934120 - Possible Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF) Attack: URL Parameter using IP Address
* 934140 - Perl Injection Attack
* 934100 - Node.js Injection Attack
APPLICATION ATTACK XSS
* 941100 - XSS Attack Detected via libinjection
* 941110 - XSS Filter - Category 1: Script Tag Vector
* 941130 - XSS Filter - Category 3: Attribute Vector
* 941140 - XSS Filter - Category 4: Javascript URI Vector
* 941160 - NoScript XSS InjectionChecker: HTML Injection
* 941170 - NoScript XSS InjectionChecker: Attribute Injection
* 941180 - Node-Validator Deny List Keywords
* 941190 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941200 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941210 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941220 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941230 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941240 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941250 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941260 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941270 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941280 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941290 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941300 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941310 - US-ASCII Malformed Encoding XSS Filter - Attack Detected
* 941350 - UTF-7 Encoding IE XSS - Attack Detected
* 941360 - JSFuck / Hieroglyphy obfuscation detected
* 941370 - JavaScript global variable found
* 941390 - Javascript method detected
* 941400 - XSS JavaScript function without parentheses
* 941101 - XSS Attack Detected via libinjection
* 941120 - XSS Filter - Category 2: Event Handler Vector
* 941150 - XSS Filter - Category 5: Disallowed HTML Attributes
* 941181 - Node-Validator Deny List Keywords
* 941320 - Possible XSS Attack Detected - HTML Tag Handler
* 941330 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941340 - IE XSS Filters - Attack Detected
* 941380 - AngularJS client side template injection detected
APPLICATION ATTACK SQLI
* 942100 - SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection
* 942140 - SQL Injection Attack: Common DB Names Detected
* 942151 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL function name detected
* 942160 - Detects blind sqli tests using sleep() or benchmark()
* 942170 - Detects SQL benchmark and sleep injection attempts including conditional queries
* 942190 - Detects MSSQL code execution and information gathering attempts
* 942220 - Looking for integer overflow attacks, these are taken from skipfish, except 2.2.2250738585072011e-308 is the "magic number" crash
* 942230 - Detects conditional SQL injection attempts
* 942240 - Detects MySQL charset switch and MSSQL DoS attempts
* 942250 - Detects MATCH AGAINST, MERGE and EXECUTE IMMEDIATE injections
* 942270 - Looking for basic sql injection. Common attack string for mysql, oracle and others
* 942280 - Detects Postgres pg\_sleep injection, waitfor delay attacks and database shutdown attempts
* 942290 - Finds basic MongoDB SQL injection attempts
* 942320 - Detects MySQL and PostgreSQL stored procedure/function injections
* 942350 - Detects MySQL UDF injection and other data/structure manipulation attempts
* 942360 - Detects concatenated basic SQL injection and SQLLFI attempts
* 942500 - MySQL in-line comment detected
* 942540 - SQL Authentication bypass (split query)
* 942560 - MySQL Scientific Notation payload detected
* 942550 - JSON-Based SQL Injection
* 942120 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL Operator Detected
* 942130 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL Boolean-based attack detected
* 942131 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL Boolean-based attack detected
* 942150 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL function name detected
* 942180 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 1/3
* 942200 - Detects MySQL comment-/space-obfuscated injections and backtick termination
* 942210 - Detects chained SQL injection attempts 1/2
* 942260 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 2/3
* 942300 - Detects MySQL comments, conditions and ch(a)r injections
* 942310 - Detects chained SQL injection attempts 2/2
* 942330 - Detects classic SQL injection probings 1/3
* 942340 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 3/3
* 942361 - Detects basic SQL injection based on keyword alter or union
* 942362 - Detects concatenated basic SQL injection and SQLLFI attempts
* 942370 - Detects classic SQL injection probings 2/3
* 942380 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942390 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942400 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942410 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942470 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942480 - SQL Injection Attack
* 942430 - Restricted SQL Character Anomaly Detection (args): # of special characters exceeded (12)
* 942440 - SQL Comment Sequence Detected
* 942450 - SQL Hex Encoding Identified
* 942510 - SQLi bypass attempt by ticks or backticks detected
* 942520 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 4.0/4
* 942521 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 4.1/4
* 942522 - Detects basic SQL authentication bypass attempts 4.1/4
* 942101 - SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection
* 942152 - SQL Injection Attack: SQL function name detected
* 942321 - Detects MySQL and PostgreSQL stored procedure/function injections
* 942251 - Detects HAVING injections
* 942490 - Detects classic SQL injection probings 3/3
* 942420 - Restricted SQL Character Anomaly Detection (cookies): # of special characters exceeded (8)
* 942431 - Restricted SQL Character Anomaly Detection (args): # of special characters exceeded (6)
* 942460 - Meta-Character Anomaly Detection Alert - Repetitive Non-Word Characters
* 942511 - SQLi bypass attempt by ticks detected
* 942530 - SQLi query termination detected
* 942421 - Restricted SQL Character Anomaly Detection (cookies): # of special characters exceeded (3)
APPLICATION ATTACK SESSION FIXATION
* 943100 - Possible Session Fixation Attack: Setting Cookie Values in HTML
* 943110 - Possible Session Fixation Attack: SessionID Parameter Name with Off-Domain Referer
* 943120 - Possible Session Fixation Attack: SessionID Parameter Name with No Referer
APPLICATION ATTACK JAVA
* 944100 - Remote Command Execution: Suspicious Java class detected
* 944110 - Remote Command Execution: Java process spawn (CVE-2017-9805)
* 944120 - Remote Command Execution: Java serialization (CVE-2015-4852)
* 944130 - Suspicious Java class detected
* 944140 - Java Injection Attack: Java Script File Upload Found
* 944150 - Potential Remote Command Execution: Log4j / Log4shell
* 944151 - Potential Remote Command Execution: Log4j / Log4shell
* 944200 - Magic bytes Detected, probable java serialization in use
* 944210 - Magic bytes Detected Base64 Encoded, probable java serialization in use
* 944240 - Remote Command Execution: Java serialization (CVE-2015-4852)
* 944250 - Remote Command Execution: Suspicious Java method detected
* 944260 - Remote Command Execution: Malicious class-loading payload
* 944300 - Base64 encoded string matched suspicious keyword
* 944152 - Potential Remote Command Execution: Log4j / Log4shell
DATA LEAKAGES
* 950130 - Directory Listing
* 950140 - CGI source code leakage
* 950100 - The Application Returned a 500-Level Status Code
DATA LEAKAGES SQL
* 951110 - Microsoft Access SQL Information Leakage
* 951120 - Oracle SQL Information Leakage
* 951130 - DB2 SQL Information Leakage
* 951140 - EMC SQL Information Leakage
* 951150 - firebird SQL Information Leakage
* 951160 - Frontbase SQL Information Leakage
* 951170 - hsqldb SQL Information Leakage
* 951180 - informix SQL Information Leakage
* 951190 - ingres SQL Information Leakage
* 951200 - interbase SQL Information Leakage
* 951210 - maxDB SQL Information Leakage
* 951220 - mssql SQL Information Leakage
* 951230 - mysql SQL Information Leakage
* 951240 - postgres SQL Information Leakage
* 951250 - sqlite SQL Information Leakage
* 951260 - Sybase SQL Information Leakage
DATA LEAKAGES JAVA
* 952100 - Java Source Code Leakage
* 952110 - Java Errors
DATA LEAKAGES PHP
* 953100 - PHP Information Leakage
* 953110 - PHP source code leakage
* 953120 - PHP source code leakage
* 953101 - PHP Information Leakage
DATA LEAKAGES IIS
* 954100 - Disclosure of IIS install location
* 954110 - Application Availability Error
* 954120 - IIS Information Leakage
* 954130 - IIS Information Leakage
WEB SHELLS
* 955100 - Web shell detected
* 955110 - r57 web shell
* 955120 - WSO web shell
* 955130 - b4tm4n web shell
* 955140 - Mini Shell web shell
* 955150 - Ashiyane web shell
* 955160 - Symlink\_Sa web shell
* 955170 - CasuS web shell
* 955180 - GRP WebShell
* 955190 - NGHshell web shell
* 955200 - SimAttacker web shell
* 955210 - Unknown web shell
* 955220 - lama's'hell web shell
* 955230 - lostDC web shell
* 955240 - Unknown web shell
* 955250 - Unknown web shell
* 955260 - Ru24PostWebShell web shell
* 955270 - s72 Shell web shell
* 955280 - PhpSpy web shell
* 955290 - g00nshell web shell
* 955300 - PuNkHoLic shell web shell
* 955310 - azrail web shell
* 955320 - SmEvK\_PaThAn Shell web shell
* 955330 - Shell I web shell
* 955340 - b374k m1n1 web shell
* 955350 - webadmin.php file manager
### Troubleshooting
#### Legitimate Requests Blocked
**Issue**: False positive blocking valid traffic
**Solution:** Contact support in Discord.sherpa.sh to have the request whitelisted.
#### WAF Not Blocking
**Issue**: Known attack getting through
**Steps**:
1. Verify WAF is in Active Mode (not Monitor)
2. Check application is routing through Sherpa.sh
3. Confirm no bypass rules are configured
4. Contact support if issue persists
#### High Latency
**Issue**: Requests taking longer than expected
**Typical Causes**:
* WAF adds \~10-20ms per request (normal)
* Challenge mode adds \~200-500ms (only for suspicious requests)
* Check application performance separately
**Verification**:
bash
```bash
# Test request timing
curl -w "@curl-format.txt" -o /dev/null -s https://yourapp.com
```
# Upstash
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Upstash
Upstash works seamlessly with Sherpa.sh. Since your application runs in a Docker container that can make outbound connections, you can connect to Upstash Redis or Upstash Kafka using your connection credentials.
## Setup
1. Create your Upstash database (Redis or Kafka) at [upstash.com](https://upstash.com)
2. Copy your connection credentials from the Upstash dashboard
3. Add the credentials as [environment variables](/getting-started/configuration#environment-variables) in your Sherpa.sh project
## Environment Variables
For **Upstash Redis**, set:
* UPSTASH\_REDIS\_REST\_URL
* UPSTASH\_REDIS\_REST\_TOKEN
For **Upstash Kafka**, set:
* UPSTASH\_KAFKA\_REST\_URL
* UPSTASH\_KAFKA\_REST\_USERNAME
* UPSTASH\_KAFKA\_REST\_PASSWORD
Your application will connect to Upstash using these credentials just like it would in any other environment.
## Getting Help
If you need help with your setup, we will help you get your application deployed free of charge. Just open a ticket with us in Discord:
[https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
# Zero Down-Time Migration
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Zero Downtime Migration
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for migrating your applications from Vercel, Netlify, AWS, or another provider to Sherpa.sh with zero downtime.
:::tip[Recommended Approach]
The recommended zero-downtime migration method is to use the [SafetyNet feature](/infrastructure/safety-net). SafetyNet provides automatic fallback to your existing provider with zero configuration complexity.
You should only use the manual load balancing methods described on this page if you cannot use SafetyNet for some reason.
Any migration can still benefit from following the recommendations in [DNS Migration Best Practices](#dns-migration-best-practices) - such as lowering TTLs before migrations.
:::
### Prerequisites
* An active Sherpa.sh account
* Access to your current hosting platform (Vercel, Netlify, AWS, etc)
* Access to your DNS provider
* Your application's source code repository
### Zero-Downtime Migration Strategy
The key to a zero-downtime migration is to set up and verify your application on Sherpa.sh **before** changing your DNS settings. This is accomplished through a parallel deployment strategy:
#### The Parallel Deployment Method
1. **Deploy to Sherpa.sh while keeping your existing deployment active**
2. **Verify functionality using Sherpa.sh temporary URLs**
3. **Implement DNS changes using a phased approach**
4. **Monitor and finalize the migration**
#### DNS Migration best practices
To avoid downtime during DNS propagation:
1. **Lower TTL values in advance**:
* At least 24-48 hours before migration, reduce the TTL (Time To Live) values for your DNS records to the minimum allowed value (often 300 seconds/5 minutes)
* This ensures faster propagation when you make the actual switch
2. **Use Sherpa.sh's preview environment**:
* Before changing production DNS, fully test your application on Sherpa.sh's preview domain. Follow the [getting started guide ](/getting-started/quickstart)to deploy your application on a preview domain
3. **Implement CNAME flattening** (if supported by your DNS provider):
* Set up CNAME records pointing to the records displayed when you setup your [custom domain](/getting-started/custom-domains) in the Sherpa.sh panel
* This provides more flexibility during the transition
4. **Use parallel DNS configuration**:
* Configure your application on Sherpa.sh to respond to your domain. For example, set allowed hosts to include your domain.
* Verify your application is working on the preview domain
### Migration Process
#### 1. Connect and deploy your app on a preview domain
Follow the [getting started guide ](/getting-started/quickstart)to deploy your application on a preview domain
#### 2. DNS Migration
* In your DNS provider:
1. Use a temporary subdomain and point it with CNAMEs to the records displayed when you setup your [custom domain](/getting-started/custom-domains) in the Sherpa.sh panel
2. Keep your existing DNS records active
3. Test the Sherpa.sh deployment using the temporary subdomain. Don't forget to add the domain to your allowed hosts or similiar setting in your application.
:::note
For example, if you run your app on **app.example.com** the temporary domain to test could be **app-temp-test.example.com.** The goal is to make sure that you are able to have records in your DNS provider point successfully to an app running on Sherpa.sh before moving your primary domain.
:::
#### 3. Migrate Traffic
For mission-critical applications, use this blue-green deployment approach:
1. Set up complete infrastructure on Sherpa.sh (the "green" environment, like you did in step 1)
2. Keep your current platform running (the "blue" environment)
3. Use a load balancer or traffic manager to control traffic distribution. Some DNS providers will allow you to do this from DNS itself. This is the recomend way.
4. Gradually shift traffic percentages from blue to green
5. Monitor for any issues and be prepared to shift back if necessary
#### 4. Testing
* Once you've traffic shifted fully to sherpa.sh, test your application.
* Keep the original deployment on your old provider active for 24-48 hours as fallback while you test the new production environment
* You can remove the old DNS records once you are confident the migration was successful.
### Troubleshooting
#### Common Issues and Solutions
**DNS Propagation Problems**
* **Issue**: Some users see the new site while others see the old one
* **Solution**: This is normal during DNS propagation. Wait 24-48 hours for full propagation, and keep both deployments active during this period.
**Missing Environment Variables**
* **Issue**: Application errors related to configuration
* **Solution**: Verify all environment variables are correctly set in Sherpa.sh dashboard
**Build Failures**
* **Issue**: Deployment fails on Sherpa.sh
* **Solution**: Check build logs and adjust configuration based on differences between platforms
**Database Connection Problems**
* **Issue**: Application cannot connect to database
* **Solution**: Verify connection strings and network access settings. You may need to allow all IPs to access your database if you are not using a sherpa.sh managed database.
#### Getting Help
If you encounter issues during migration, contact Sherpa.sh support in discord:
[https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
# Clerk
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Clerk
When using Clerk with Sherpa.sh you there are a few caveats to be aware of. Because Sherpa.sh is a serverful environment where your app runs inside of a Docker container, your application is going to see `localhost` whenever it queries your hostname.
This means you have to explicitly tell Clerk the return URLs in your environment settings to match the domain that you're using with sherpa.sh
## Next.js Projects:
You need to set these [environment variables](/getting-started/configuration#environment-variables) on any project using Clerk
* NEXT\_PUBLIC\_clerk\_SIGN\_IN\_FORCE\_REDIRECT\_URL
* NEXT\_PUBLIC\_clerk\_SIGN\_UP\_FORCE\_REDIRECT\_URL
* NEXT\_PUBLIC\_clerk\_SIGN\_IN\_FALLBACK\_REDIRECT\_URL
* NEXT\_PUBLIC\_clerk\_SIGN\_UP\_FALLBACK\_REDIRECT\_URL
Typically, these can all be the same value, and that value is usually the homepage of your application. But this will all depend on your particular Clerk, set up in your application.
## Getting Help
If you need help with your setup, we will help you get your application deployed free of charge. Just open a ticket with us in Discord:
[https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
# Astro
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Astro
Deploy your Astro applications with zero configuration and blazing-fast performance. Our platform is specifically optimized for Astro's unique architecture, delivering the fastest possible page loads and optimal user experiences for content-focused sites.
### Why Sherpa is Perfect for Astro
#### Zero Edge Request Charges
Unlike other platforms that charge per edge request, we never bill for edge traffic. This is especially important for Astro sites because of the framework's islands architecture:
```javascript
Astro creates highly optimized, minimal bundles
// page.html (12kb) - Pre-rendered HTML content
// island-header.js (3kb) - Interactive header component
// island-cart.js (5kb) - Shopping cart island
// island-search.js (2kb) - Search functionality
```
**Why This Saves You Money:**
* Astro's islands architecture creates multiple small JavaScript bundles for interactive components
* Each island loads independently, generating separate edge requests
* Static assets (images, fonts, CSS) create additional edge requests
* Other platforms charge $0.01-0.10 per 10,000 edge requests
* **With sherpa.software: $0.00 for unlimited edge requests**
**Real-World Impact:**
Astro Content Site Monthly Traffic Overview
Static Pages: Approximately 3 million requests for pre-rendered HTML
Island Components: Approximately 1.5 million requests for interactive JS
Images & Assets: Approximately 4 million requests
API Calls: Approximately 500,000 requests
Cost Comparison
Other Platforms: $200-400/month in edge fees
Sherpa.sh: $0
#### Optimized for Static-First Performance
We've fine-tuned our infrastructure specifically for Astro's static-first approach with optional SSR:
**Performance Optimizations**
* **Instant Page Loads**: Static HTML served from edge locations worldwide
* **Island Hydration**: Lightning-fast partial hydration of interactive components
* **Asset Optimization**: Automatic compression and caching for all static assets
* **Build Caching**: Intelligent build caching reduces deployment times by 40-60%
**Performance Benchmarks:**
# Time to First Byte (TTFB) - 95th percentile
sherpa.software: 42ms average globally
Traditional VPS: 280ms average
Other static hosts: 95ms average
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
### Quick Start Guide
Get your Astro site live in under 2 minutes with our streamlined deployment process.
#### Prerequisites
* Astro 5.x project
* Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket)
* Node.js 18+ locally for development
#### Deployment Steps
1. **Connect Repository**: Link your Git repository to sherpa.software
2. **Auto-Detection**: We automatically detect your Astro configuration
3. **Deploy**: Push to your main branch triggers automatic deployment
4. **Live**: Your site is available at `https://your-site.sherpa.software`
#### What You Get Instantly
* **Zero Configuration**: Works with your existing `astro.config.mjs`
* **Global CDN**: All assets served from 200+ edge locations
* **Automatic HTTPS**: SSL certificates provisioned and renewed automatically
* **Image Optimization**: Built-in support for Astro's Image component
* **Content Collections**: Full support for type-safe content management
* **Pay-per-Use**: No idle costs - only pay for actual usage
:::note
**By default CDN caching is on:** Static pages are cached at the edge for maximum performance. For SSR routes, [set cache-control headers](https://docs.astro.build/en/guides/server-side-rendering/#response-headers) on pages that need dynamic content. Please see our [CDN Docs](/infrastructure/cdn-and-caching/) for more info on cache-control headers.
:::
### Configuration
#### Static Site Configuration
For static builds, ensure you are **not** using any adapters in your `astro.config.mjs` file:
```js
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'static', // Default static output
// Do not include any adapter
});
```
#### Server-Side Rendering Configuration
For server-side rendering, you must use the `@astrojs/node` adapter in `standalone` mode:
```bash
# Install the Node adapter
npm install @astrojs/node
```
```js
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import node from '@astrojs/node';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server', // or 'hybrid' for mixed static/SSR
adapter: node({
mode: 'standalone'
})
});
```
:::note
**For SSR/Hybrid mode:** The `@astrojs/node` adapter in `standalone` mode is required. Other adapters are not currently supported.
:::
#### Astro Islands Architecture Benefits
**Minimal JavaScript Delivery**
Astro's islands architecture works perfectly with our infrastructure:
```astro
---
// Islands load only when needed
import Header from '../components/Header.astro';
import InteractiveCart from '../components/Cart.jsx'; // React island
import SearchBar from '../components/Search.vue'; // Vue island
---
```
**Benefits on sherpa.software:**
* **Zero Hydration Cost**: Static components require no JavaScript
* **Selective Hydration**: Islands hydrate only when needed
* **Framework Agnostic**: Mix React, Vue, Svelte, Solid in one project
* **Edge Caching**: HTML cached globally, islands cached per component
### Advanced Features
#### Content Collections
Astro's Content Collections work seamlessly with sherpa.software:
```typescript
// src/content/config.ts
import { defineCollection, z } from 'astro:content';
const blog = defineCollection({
type: 'content',
schema: z.object({
title: z.string(),
pubDate: z.date(),
author: z.string()
})
});
export const collections = { blog };
```
**Platform Benefits:**
* **Type-Safe Content**: Full TypeScript support during builds
* **Fast Builds**: Content collection parsing optimized for speed
* **Git-Based Workflow**: Content updates trigger automatic rebuilds
* **Global Distribution**: All content served from edge locations
#### Image Optimization
Astro's Image component is fully optimized on sherpa.software:
```astro
---
import { Image } from 'astro:assets';
import heroImage from '../assets/hero.jpg';
---
```
**Optimization Features:**
* WebP/AVIF conversion for modern browsers
* Responsive image generation
* Lazy loading support
* Global CDN delivery
* Build-time optimization
#### Hybrid and Server Rendering
Full support for Astro's SSR and hybrid modes using the Node adapter:
```js
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import node from '@astrojs/node';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'hybrid', // Static by default, opt-in to SSR per page
adapter: node({ mode: 'standalone' })
});
```
**SSR Performance:**
* **Fast Cold Starts**: Pre-warmed Node.js instances
* **Auto-Scaling**: Scales based on traffic patterns
* **Edge Caching**: Intelligent caching for SSR responses
#### Caching Strategy
**Intelligent Cache Headers**
We optimize caching based on your content type:
```bash
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable # Static assets (JS, CSS, images)
Cache-Control: public, max-age=3600 # Static HTML pages
Cache-Control: public, s-maxage=60, stale-while-revalidate # SSR pages
```
**Cache Debugging**
Check cache performance in browser DevTools:
```bash
# Response headers show cache status
Cdn-Cache: HIT # Served from edge cache
Cdn-Cache: MISS # Fetched from origin
```
### Developer Experience
#### Local Development Compatibility
Your local development workflow remains unchanged:
```bash
# Development (unchanged)
npm run dev
# Build locally (unchanged)
npm run build
# Preview locally (unchanged)
npm run preview
# Deploy to sherpa.software
git push origin main # Triggers automatic deployment
```
#### Build Process Insights
Monitor your builds in real-time:
* **Build Time**: Typical Astro builds complete in 20-45 seconds
* **Content Processing**: See content collection parsing time
* **Asset Optimization**: Track image and asset processing
* **Bundle Analysis**: View JavaScript bundle sizes per island
#### Debugging & Monitoring
**Real-Time Logs**
View live application logs from inside the portal. You get logging for:
* **CDN requests**
* **Build output**
* **SSR requests** (if using hybrid/server mode)
* **Error tracking**
### Configuration Examples
#### Multi-Framework Islands
Leverage Astro's ability to mix frameworks:
```astro
---
import ReactCounter from './Counter.jsx';
import VueCalendar from './Calendar.vue';
import SvelteChart from './Chart.svelte';
---
```
**All frameworks work seamlessly on sherpa.software with zero additional configuration.**
#### View Transitions
Astro's View Transitions API works perfectly:
```astro
---
import { ViewTransitions } from 'astro:transitions';
---
```
#### Custom Integrations
All Astro integrations are supported:
```js
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import mdx from '@astrojs/mdx';
import sitemap from '@astrojs/sitemap';
import partytown from '@astrojs/partytown';
export default defineConfig({
integrations: [mdx(), sitemap(), partytown()]
});
```
### Enterprise Features
#### Advanced Security
* **SOC 2 Compliance**: Enterprise-grade security controls
* **Custom WAF Rules**: Protect against application-specific threats
* **DDoS Protection**: Automatic traffic filtering and rate limiting
#### Performance & Reliability
* **100% Uptime SLA**: Guaranteed uptime with financial backing
* **Custom Edge Logic**: Run code at 200+ global locations
* **Dedicated Infrastructure**: Isolated compute for enterprise workloads
#### Developer Support
* **Dedicated Account Manager**: Direct line to platform experts
* **Priority Support**: <2 hour response time for critical issues
* **Custom Integrations**: Connect with your existing DevOps tools
### Troubleshooting
#### Getting Help
* **Documentation**: Comprehensive guides here
* **Community Support & Tickets**: Join our [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
### Migration Guide
#### From Other Platforms
The easiest way to migrate from another platform is to follow the [quickstart guide](#quick-start-guide).
* [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
* [Connect Github](../../getting-started/quickstart#step-2-link-your-github)
* [Configure your application settings](../../getting-started/configuration)
#### From Static Hosts
Key differences when migrating from traditional static hosts:
* **SSR Support**: Optionally enable hybrid or server mode with `@astrojs/node` adapter
* **Build Caching**: Faster rebuilds with intelligent caching
* **Island Optimization**: Better performance for interactive components
* **Unified Platform**: No need for separate services for SSR
* **Adapter Requirement**: Use standalone mode for the Node adapter if using SSR/hybrid
### Next Steps
After deploying your first Astro site:
1. **Custom Domain**: Connect your domain in the dashboard
2. **Environment Variables**: Configure secrets and API keys
3. **Content Collections**: Set up your content structure
4. **Team Access**: Invite collaborators with role-based permissions
5. **Monitoring**: Set up alerts for performance and errors
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
# Custom Setups
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Custom Setups
:::note
**Need something else?** We are always happy to tailor our services for your specific use case. We want to be your partner, because when you succeed, we succeed.
Please [contact us](https://www.sherpa.sh/contact) with more details about your use case, and lets make it happen!
:::
# Docker
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Docker
We've deployed thousands of containerized applications at scale and have optimized the sherpa.sh infrastructure for maximum Docker performance. When deploying Docker containers to sherpa.sh you get additional performance and scalability benefits you wouldn't get when self-hosting - with zero-configuration - thanks to our container-optimized architecture.
### Supported Frameworks
If it works in a Docker container on your machine, it works on sherpa.sh. Full stop. No magic tricks, no obscure configuration requirements – just containers doing what containers do best: containing things.
Popular frameworks we've seen deployed (but certainly not limited to):
* Django
* Rails
* Laravel
* Express.js
* Flask
* Spring Boot
* FastAPI
* Phoenix
* ASP.NET Core
* Strapi
* NestJS
We've even seen people containerize legacy Yesod (Haskell) applications. We didn't ask why, and neither should you.
### Supported Features
| Feature | Support |
| -------------------------- | --------------- |
| Custom Dockerfile | ✅ |
| Multistage builds | ✅ |
| Custom port configuration | ✅ |
| Environment variables | ✅ |
| Secrets management | ✅ |
| Autoscaling scale | ✅ |
| Multi region deployment | Enterprise Only |
| Blue/green deployment | ✅ |
| Health checks | ✅ |
| Container logs | ✅ |
| Custom resource allocation | ✅ |
### Docker Quickstart
To deploy your first Docker container, follow our [quick start guide.](../../getting-started/quickstart) Your container will be live in \~2 minutes.
What you get out of the box:
* Zero-configuration deployments that just work
* Automatic HTTPS and custom domain support
* Built-in performance optimization
* Global, production-ready infrastructure that can scale
* Never pay for idle instances. Only pay for what you use
### Architecture
To maximize performance - and savings - we build and deploy your Docker containers using our optimized infrastructure. When you push your code, we:
1. Detect your Dockerfile in your repository
2. Build your container image in the same directory as your Dockerfile
3. Deploy to your configured region(s)
4. Auto-scale horizontally based on traffic patterns. Has traffic increases we spend up more containers. As traffic decreases we spin down those containers.
### Configuration
We believe in convention over configuration. Your existing Dockerfile works immediately - no additional setup required. When you need customization, our platform stays flexible.
#### Dockerfile Requirements
* Your Docker file can use any name. It doesn't have to be `Dockerfile` . Just specify it in the settings.
* Must expose a port via the `EXPOSE` instruction. You must set this value inside of the application settings.
* Should follow Docker best practices for layer caching and image size. This is not necessary. It will just help speed up your build time.
### CDN Integration
All Docker container deployments are automatically placed behind our global CDN. This provides:
1. **Automatic static asset caching**: The CDN respects any cache-control headers returned by your application
2. **Framework-specific optimizations**: Our CDN will automatically cache the static assets the application you are using as long as they are served over HTTP from the Docker container. This will work out the box for most frameworks.\
\
**Django Example**:\
For Django applications, static files served from your `/static/` directory will automatically be cached by the CDN according to your cache headers. For optimal performance, set:
```python
pythonCopy# settings.py
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_STORAGE = 'django.contrib.staticfiles.storage.ManifestStaticFilesStorage'
```
\
**Rails Example**:\
For Rails applications, assets compiled with the asset pipeline will be cached by the CDN. Configure your production environment with:
```ruby
rubyCopy# config/environments/production.rb
config.public_file_server.headers = {
'Cache-Control' => 'public, max-age=31536000'
}
config.assets.compile = false
config.assets.digest = true
```
### Auto-scaling
Your containers automatically scale based on traffic patterns:
* **Scale up**: New container instances are provisioned when traffic increases
* **Scale down**: Unused containers are gracefully terminated when traffic decreases
### Enterprise Features
Have a unique need? Our enterprise features deliver additional capabilities:
* **Multi-region deployments**: Deploy your containers to multiple geographic regions for global performance
* **Custom build configurations**: Have a special need? We can customize our platform
* **Advanced security features**: If you need SOC II, HIPAA, or FedRamp certified deployments
* **Dedicated support staff**: Dedicated account manager and support engineers for your company's unique needs
# Next.js
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Next.js
We've deployed thousands of Next.js applications at scale and have optimized the sherpa.sh infrastructure for maximum Next.js performance.
When deploying Next.js to sherpa.sh you get additional performance and scalability benefits you wouldn't get when self-hosting - with zero-configuration - thanks to our [framework-defined architecture](/infrastructure/architecture)
:::note
Read more about how we run Next.js at scale in our blog post:
Secrets of Self-hosting Nextjs at Scale
:::
## Next.js Quickstart
To deploy your first Next.js application, follow our [quick start guide](../../getting-started/quickstart). Your app will be live in \~2 minutes.
What you get out of the box:
* Zero-configuration deployments that just work
* Automatic HTTPS and custom domain support
* Built-in performance optimization
* Global, production-ready infrastructure that can scale.
Never pay for idle instances. Only pay for what you use.
## Supported Versions
* Next.js 15
* Next.js 14
## Supported Features
Feature
Supported by sherpa.sh
App Router
✅
Page Router
✅
Middleware functions
✅
Edge V8 Isolates
Enterprise Only
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
✅
Server Side Rendering (SSR)
✅
Static Site Generation (SSG)
✅
Partial Pre-Rendering (PPR)
✅
Layout (Nested, Parallel, Error)
✅
Data Fetching Revalidate (10, 60)
✅
Data Fetching (no-store, POST default, POST without cache)
✅
Routing (default, no-cache)
✅
Static Metadata
✅
Dynamic Metadata (SSG, SSR)
✅
Image Optimization
✅
Server Actions
✅
## Architecture
To maximize performance - and savings - we use framework defined infrastructure to deploy your app. You can read about our infrastructure setup in more detail on the [Next.js Architecture](#architecture) page.
## Configuration
We believe in convention over configuration. Your existing `next.config.js` works immediately - no additional setup required. When you need customization, our platform stays flexible.
### next.config.js overrides
To prepare your application for our infrastructure, the sherpa.sh platform will override some of the values in your projects `next.config.js`file. Below you will find descriptions of the overridden values:
* **assetPrefix**: We deploy your static assets to a specialized static CDN. We override the `assetPrefix`so your app knows to ask the CDN for your static files.
* **generateBuildId**: We set a unique hash for each build that correlates with a deployment in the sherpa.sh portal.
* **cacheHandler**: We maintain a globally distributed cache to enhance performance of PPR, ASO, and other caching functionality of Next.js. Each application gets a slice of the cache. This is our custom handler for read/write/delete to your applications portion of the cache.
* **cacheMaxMemorySize**: Set to 0 because your application will use the global cache.
* **headers**: We append a `cache-control`header to your existing `next.conf.js`headers for static asset caching best practices. If you need custom control over this header, you can configure it from inside the portal.
* **output**: This always is set to `standalone`to minimize deployment bundles and make deployments compatible with our global infrastructure.
* **allowedOrigins**: Set to a wildcard of your apps domain `*.[YOUR_DOMAIN]` to ensure your server actions and other Next.js functionality works in the global deployment setup.
## Image Optimization
By default, sherpa.sh supports image optimization and respects all your Next.js config settings. Optimized images are stored in our global cache infrastructure and then served by our CDN until the content goes stale based on the `cache-control headers` sent by Next.js to the CDN.
:::note
**CDN Caching Query Params:** By default, sherpa.sh will cache each individually optimized image separately in the CDN. For example, an image `logo.svg` that is loaded with two seaprate widths `100`and `200`via the query params, will have the two separate images stored in the CDN. \
\
If you need to ignore specific query params, let us know. We can customize your setup.
:::
## Caching
By default our CDN will respect the cache control headers returned by Nextjs to the CDN. (Our CDN sits in front of the entire next application, for more info read about our [architecture](#architecture)). With one caveat. Any endpoints at `/api/*` will never get cached by the CDN or the browser. Our setup will override ignore any cache-control headers on API endpoints.
:::tip
If you want to see if a particular page or asset (JS, CSS, Image, etc) is being cached. You can look at the response headers of the request in developer tools for the `Cdn-Cache` header which will tell you if its a cache `HIT` or cache `MISS`. This info for historic requests are also available in the logging section of your portal.
:::
## Architecture
## Overview
Our NextJS framework-defined architecture delivers exceptional performance and cost efficiency through a carefully designed system of CDNs, Kubernetes clustering, and distributed caching. This document explains how these components work together to serve your application.
### Global Content Delivery
Your application sits behind a global CDN that acts as the primary entry point for all incoming requests. This CDN intelligently processes the cache headers returned by NextJS (`cache-control`, `stale-while-revalidate`, etc), ensuring that as many requests as possible are served directly from the CDN's edge locations. The result is not just blazing-fast response times for your users, but also significant cost savings through our strategic CDN partnerships.
### Application Deployment
We host your application in our scalable Kubernetes clusters. As request volume increases, our system automatically scales up your application's functions behind a load balancer. This ensures smooth handling of traffic spikes while maintaining consistent performance. The containerized nature of the deployment means your application runs in identical environments across all instances, eliminating environment-related issues.
### Static Asset Management
Static assets are served through a dedicated CDN, accessible via a `static-` subdomain prefix. This separation is achieved by configuring the NextJS `assetPrefix` variable during build time (See [configuring Next.js](#configuration)). Our default caching settings for static assets are optimized for common use cases, striking a balance between performance and freshness. Soon, you'll be able to customize these settings through our portal to match your specific needs.
### Advanced Caching System
We've implemented a sophisticated caching system that's co-located with your application deployment. At its heart is a custom `cache-handler.js` file that enables your NextJS application to quickly read and write cache data using our global caching servers. This setup ensures optimal performance and allows us to scale your application seamlessly within our Kubernetes infrastructure.
### Performance and Scaling
Performance optimization happens at multiple levels in our architecture. The CDN layer maximizes cache hits while ensuring content freshness. When traffic increases, your application scales horizontally in our Kubernetes clusters, with new instances spinning up automatically to meet demand. The multi-layered caching approach combines CDN-level caching for edge performance, application-level caching for dynamic content, and static asset caching for resource optimization.
### Configuration Best Practices
Our system comes with sensible defaults, but it ultimately respects the settings inside of Next.js. In most cases the default Next.js settings will provide optimum performance. That said, you have full control via Next.js and any cache-headers and performance settings you configure will be respected by our framework-defined architecture
## Enterprise Features
Have a unique need? Our enterprise features deliver additional capabilities:
* Edge runtime capabilities: Run your middleware at the edge in v8 isolates.
* Custom deployment configurations: Have a special need? We can customize our platform.
* Advanced security features: If you need SOC II, HIPAA, or FedRamp certified deployments.
* Dedicated support staff: Dedicated account manager and support engineers for your company's unique needs.
# Payload CMS
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
Deploy PayloadCMS Applications with Zero Configuration
# Payload CMS
Deploy your PayloadCMS applications with zero configuration and enterprise-grade performance. Our platform is specifically optimized for PayloadCMS architecture, delivering faster builds and better runtime performance than traditional hosting solutions.
### Why sherpa.sh is Perfect for PayloadCMS
#### Optimized Node.js Performance for PayloadCMS
We've fine-tuned our infrastructure specifically for PayloadCMS's Express.js architecture to deliver optimal performance:
**PayloadCMS Performance Optimizations:**
* **Cold Start Elimination:** Pre-warmed Node.js instances across regions
* **Memory Optimization:** 1GB-4GB+ containers with intelligent horizontal scaling behind a loadbalancer
* **Smart caching:** Where we autodetect admin view and non cachable API endpoints to ensure consistent FAST performance across both the client and admin experience.
* **Database Optimization:** Connection pooling for MongoDB/PostgreSQL
* **Admin Panel Speed:** Optimized static asset delivery for Payload admin UI
**Performance Benchmarks:**
```bash
# API response times (95th percentile)
sherpa.sh: 120ms average globally
PayloadCMS Cloud: 280ms average
Traditional VPS: 450ms average
Other serverless: 320ms average (with cold starts)
```
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up)
### Quick Start Guide
Get your PayloadCMS app live in under 5 minutes with our streamlined deployment process.
#### Prerequisites
* PayloadCMS 2.x project
* Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket)
* Node.js 18+ locally for development
* MongoDB or PostgreSQL database
#### Deployment Steps
1. **Connect Repository:** Link your Git repository to sherpa.sh
2. **Auto-Detection:** We automatically detect your PayloadCMS configuration
3. **Database Setup:** Configure your database connection string
4. **Deploy:** Push to your main branch triggers automatic deployment
5. **Live:** Your app is available at `https://your-app.sherpa.software`
Follow our [Quickstart Steps](#quick-start-guide) for more details.
#### What You Get Instantly
* **Zero Configuration:** Works with your existing `payload.config.ts`
* **Global CDN:** Admin UI and API served from 200+ edge locations
* **Automatic HTTPS:** SSL certificates provisioned and renewed automatically
* **Database Integration:** Seamless MongoDB/PostgreSQL connections with our managed databases
* **File Storage:** Built-in media handling without S3 complexity
* **Pay-per-Use:** No idle costs - only pay for actual usage
### Platform Optimizations
#### Automatic Configuration Enhancements
When you deploy to sherpa.sh, we automatically optimize your configuration for maximum performance:
**payload.config.ts Optimizations:**
```typescript
// Your original config is preserved, but we enhance it:
export default buildConfig({
serverURL: process.env.PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_SERVER_URL, // Auto-configured
admin: {
user: Users.slug,
bundler: webpackBundler(),
// Static assets automatically served from global CDN
},
collections: [
Users,
Media,
],
typescript: {
outputFile: path.resolve(__dirname, 'payload-types.ts'),
},
graphQL: {
schemaOutputFile: path.resolve(__dirname, 'generated-schema.graphql'),
},
db: mongooseAdapter({
url: process.env.DATABASE_URI, // Auto-configured from dashboard if selected
}),
})
```
**Environment Variables Set Automatically:**
```bash
PORT=3000 # Standard runtime port
DATABASE_URI=your-database-connection # From dashboard config
PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_SERVER_URL=https://your-app.sherpa.sh
NODE_ENV=production # Production optimizations
```
#### Performance Enhancements
**Admin Panel Optimization:**
PayloadCMS admin interface loads faster with our HTTP/2 infrastructure:
* **Bundle Splitting:** Admin UI chunks load in parallel
* **Asset Caching:** Long-term caching for unchanged admin assets
* **GraphQL Optimization:** Intelligent query caching and optimization
**File Delivery Acceleration:**
* **Automatic CDN Integration:** S3 files served globally with <50ms load times
### Advanced Features
#### Database Management
Seamless integration with your preferred database:
**MongoDB Setup:**
```typescript
// In your payload.config.ts
import { mongooseAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-mongodb'
export default buildConfig({
db: mongooseAdapter({
url: process.env.DATABASE_URI,
// Connection pooling and optimization handled automatically
}),
})
```
**PostgreSQL Setup:**
```typescript
// In your payload.config.ts
import { postgresAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-postgres'
export default buildConfig({
db: postgresAdapter({
pool: {
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URI,
}
}),
})
```
**Optimization Features:**
* **WebP/AVIF conversion** for modern browsers
* **Responsive sizing** based on device
* **Automatic compression** without quality loss
* **Global CDN delivery** for all media files
#### Caching Strategy
Intelligent cache headers optimized for PayloadCMS:
```bash
# Automatic cache configuration
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable # Static assets (admin UI)
Cache-Control: public, max-age=3600 # Collection data (configurable)
Cache-Control: private, no-cache # Admin sessions
Cache-Control: no-store # Draft content
```
### Developer Experience
#### Local Development Compatibility
Your local development workflow remains unchanged:
```bash
# Development (unchanged)
npm run dev
# Build locally (unchanged)
npm run build
# Deploy to sherpa.sh
git push origin main # Triggers automatic deployment
```
#### Build Process Insights
Monitor your builds in real-time:
* **Build Time:** Typical PayloadCMS builds complete in 2-4 minutes
* **Bundle Analysis:** See which collections contribute to bundle size
* **Database Migration:** Automatic schema updates on deployment
#### Debugging & Monitoring
Real-time application monitoring:
* **API Logs:** Track collection queries and mutations
* **Admin Activity:** Monitor user login and content changes
* **Error Tracking:** Automatic error logging with stack traces
* **Performance Metrics:** Database query performance and response times
### Configuration Examples
#### Custom Collections
Deploy complex PayloadCMS schemas without configuration issues:
```typescript
// Complex collection with relationships
const Posts = {
slug: 'posts',
admin: {
useAsTitle: 'title',
},
fields: [
{
name: 'title',
type: 'text',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'content',
type: 'richText',
},
{
name: 'author',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'users',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'featuredImage',
type: 'upload',
relationTo: 'media',
},
],
}
```
#### Environment-Specific Configuration
```typescript
// Different configs per environment
const config = buildConfig({
admin: {
user: Users.slug,
meta: {
titleSuffix: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? ' - CMS' : ' - Dev CMS'
}
},
})
```
### Enterprise Features
#### Advanced Security
* **SOC 2 Compliance:** Enterprise-grade security controls
* **Custom WAF Rules:** Protect against CMS-specific threats
* **DDoS Protection:** Automatic traffic filtering and rate limiting
* **Admin Access Control:** IP whitelisting for admin panel access
#### Performance & Reliability
* **100% Uptime SLA:** Guaranteed uptime with financial backing
* **Database Backups:** Automated daily backups with point-in-time recovery
* **Horizontal Scaling:** Auto-scale based on API traffic and admin usage
* **Content Delivery:** Global edge caching for collection data
#### Developer Support
* **Dedicated Account Manager:** Direct line to PayloadCMS experts
* **Priority Support:** <2 hour response time for critical issues
* **Migration Assistance:** Free migration from PayloadCMS Cloud
* **Custom Integrations:** Connect with your existing DevOps tools
### Troubleshooting
#### Common Issues
**Build Failures:**
```bash
# Check your payload.config.ts for syntax errors
npm run build
# Verify all dependencies are listed in package.json
npm install
```
**Database Connection Issues:**
```bash
# Verify DATABASE_URI environment variable
echo $DATABASE_URI
# Test connection locally
npm run payload migrate
```
#### Getting Help
* **Documentation:** Comprehensive guides at [docs.sherpa.sh](https://sherpa-sh.gitbook.io/sherpa.sh-docs)
* **Community Support:** Join our [Discord](https://discord.gg/sherpa)
* **Priority Tickets:** Available for paid plans
### Migration Guide
#### From PayloadCMS Cloud
The easiest way to migrate from PayloadCMS Cloud:
1. **Export Data:** Use Payload's built-in export functionality
2. **Follow Quickstart:** Connect your existing repository
3. **Import Data:** Use Payload's import functionality
4. **Update DNS:** Point your domain to sherpa.sh
#### From Self-Hosted
Key differences when migrating from self-hosted PayloadCMS:
* Remove Docker/PM2 configurations
* Environment variables managed in dashboard
* No need for reverse proxy setup (nginx/Apache)
* Automatic SSL certificate management
* Built-in file storage (no S3 configuration)
### Next Steps
After deploying your first PayloadCMS app:
1. **Custom Domain:** Connect your domain in the dashboard
2. **Environment Variables:** Configure API keys and secrets
3. **Team Access:** Invite content editors with role-based permissions
4. **Monitoring:** Set up alerts for API performance and errors
5. **Database Setup:** Connect production MongoDB/PostgreSQL
6. **Content Migration:** Import existing content and media
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up)
# Nuxt.js
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Nuxt.js
Deploy your Nuxt.js applications with zero configuration and enterprise-grade performance. Our platform is specifically optimized for Nuxt's Nitro engine and universal rendering capabilities, delivering faster builds and superior runtime performance compared to traditional hosting solutions.
### Why Sherpa.sh is Perfect for Nuxt.js
#### Zero Edge Request Charges for Nitro's Smart Chunking
Unlike other platforms that charge per edge request, we never bill for edge traffic. This is crucial for Nuxt.js applications because of Nitro's intelligent optimization strategy.
Nuxt 3's Nitro engine automatically creates numerous optimized chunks during the build process:
```javascript
// Example Nitro build output:
// .nuxt/dist/server/chunks/nitro/node-server.mjs (8kb) - Server runtime
// .nuxt/dist/client/_nuxt/entry.js (12kb) - App entry point
// .nuxt/dist/client/_nuxt/index-a1b2c3.js (4kb) - Home page component
// .nuxt/dist/client/_nuxt/about-d4e5f6.js (3kb) - About page component
// .nuxt/dist/client/_nuxt/composables-g7h8i9.js (2kb) - Auto-imported utilities
```
**Why This Matters:**
* Nitro generates 30-80+ optimized chunks per application
* Each chunk loads on-demand with intelligent code splitting
* Other platforms charge $0.01-0.10 per 10,000 edge requests
* With Sherpa.sh: $0.00 for unlimited edge requests
**Real-World Cost Impact:**
```
Monthly Traffic for Typical Nuxt App:
- Static Assets: 3 million requests (JS chunks, CSS, images)
- SSR Pages: 800,000 requests
- API Routes: 1.2 million requests
- ISR Updates: 200,000 requests
Cost Comparison:
- Other Platforms: $200-400/month in edge fees
- Sherpa.sh: $0
```
#### Optimized Nitro Engine Performance
We've fine-tuned our infrastructure specifically for Nuxt's Nitro server engine to deliver optimal universal rendering performance:
**Performance Optimizations:**
* **Cold Start Elimination**: Pre-warmed Nitro instances across global regions
* **Memory Optimization**: 1GB-4GB+ containers with intelligent auto-scaling
* **Request Routing**: Smart load balancing optimized for Nuxt's file-based routing
* **Vue Hydration**: Optimized client-side hydration with reduced layout shifts
**Performance Benchmarks:**
```
Universal Rendering Response Times (95th percentile):
- Sherpa.sh: 76ms average globally
- Traditional VPS: 380ms average
- Other serverless: 220ms average (including cold starts)
```
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up)
### Quick Start Guide
Get your Nuxt.js app live in under 2 minutes with our streamlined deployment process.
#### Prerequisites
Before deploying, ensure you have:
* **Nuxt.js 3.x+ project**
* **Git repository** hosted on GitHub
* **Node.js 18+** installed locally for development
* **Package.json** with proper build scripts configured
#### Deployment Steps
**Step 1: Connect Repository**\
Link your Git repository to Sherpa.sh through our dashboard. We support Github and automatically sync with your repository.
**Step 2: Auto-Detection**\
Our system automatically detects your Nuxt configuration by analyzing:
* `nuxt.config.ts` or `nuxt.config.js` file
* Package.json dependencies and scripts
* Project structure and routing setup
**Step 3: Configure Build Settings**\
We automatically configure optimal build settings, but you can customize:
* Build command (defaults to `npm run build`)
* Environment variables
* Node.js version
* Custom headers and redirects
**Step 4: Deploy**\
Push to your main branch to trigger automatic deployment. Our system will:
* Install dependencies
* Run the Nitro build process
* Deploy to global edge locations
* Provision SSL certificates
**Step 5: Go Live**\
Your app becomes available at `https://your-app.sherpa.software` with full CDN distribution.
#### What You Get Instantly
* **Zero Configuration**: Works with your existing `nuxt.config.ts` without modifications
* **Global CDN**: Static assets served from 200+ edge locations worldwide
* **Automatic HTTPS**: SSL certificates provisioned and auto-renewed
* **Universal Rendering**: Full support for SSR, SSG, SPA, and ISR modes
* **Pay-per-Use**: No idle costs - only pay for actual compute and bandwidth usage
### Platform Optimizations
#### Automatic Nitro Configuration
When you deploy to Sherpa.sh, we automatically enhance your Nitro configuration for maximum performance while preserving your existing settings.
**Enhanced Configuration:**
```typescript
// Your original nuxt.config.ts is preserved, but we add optimizations:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
preset: 'node-server', // Optimized for our infrastructure
},
// Your existing configuration remains unchanged
css: ['~/assets/css/main.css'],
modules: ['@nuxtjs/tailwindcss']
})
```
**Environment Variables Set Automatically:**
```bash
# Runtime environment variables configured by Sherpa.sh
PORT=3000 # Standard runtime port
HOST=0.0.0.0 # Bind to all network interfaces
NODE_ENV=production # Enable production optimizations
```
#### Performance Enhancements
**Nitro's Code Splitting Integration:**\
Nuxt's automatic code splitting works seamlessly with our HTTP/3 infrastructure:
* **Route-based Splitting**: Each page component loads independently for optimal performance
* **Composable Splitting**: Auto-imported utilities are bundled in separate, cacheable chunks
* **Plugin Splitting**: Nuxt plugins are optimized for parallel loading and execution
**Static Asset Acceleration:**
* **File Hashing**: Immutable file names with content hashes for aggressive caching
* **Multi-format Compression**: Automatic Brotli, Gzip, and deflate compression
* **Edge Caching**: Assets cached globally with sub-50ms load times
* **HTTP/3 Support**: Latest protocol for faster asset delivery
**Pre-rendering and ISR Support:**\
Enable static generation and incremental regeneration for optimal performance:
```typescript
// pages/blog/[slug].vue - Static pre-rendering
```
### Advanced Features
#### Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
Nuxt 3's ISR capabilities work perfectly with Sherpa's intelligent caching infrastructure. Configure different caching strategies for different route patterns:
```typescript
// nuxt.config.ts - Advanced route rules
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
routeRules: {
// Static pages - pre-rendered at build time
'/': { prerender: true },
'/about': { prerender: true },
// Blog posts - ISR with 1-hour cache
'/blog/**': {
prerender: true,
headers: { 'cache-control': 's-maxage=3600' }
},
// Product pages - ISR with 5-minute cache
'/products/**': {
isr: 300, // Regenerate every 5 minutes
headers: { 'cache-control': 's-maxage=300, stale-while-revalidate=60' }
},
// API routes - Dynamic with caching
'/api/**': {
cors: true,
headers: { 'cache-control': 'max-age=300' }
},
// Admin area - Always dynamic, no caching
'/admin/**': {
ssr: false,
index: false,
headers: { 'cache-control': 'no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate' }
}
}
}
})
```
**ISR Benefits:**
* **Faster Builds**: Only rebuild changed pages instead of entire site
* **Fresh Content**: Automatically update cached pages when content changes
* **Reduced Server Load**: Serve cached pages while regenerating in background
* **SEO Optimization**: Pre-rendered pages for better search engine indexing
#### Image Optimization
Automatic image optimization works seamlessly with Nuxt's built-in `` component:
```vue
```
**Optimization Features:**
* **Format Conversion**: Automatic WebP and AVIF conversion for modern browsers
* **Responsive Sizing**: Generate multiple sizes based on device capabilities
* **Lazy Loading**: Built-in intersection observer for performance
* **Global CDN**: Optimized images served from nearest edge location
* **Quality Optimization**: Intelligent quality adjustment based on image content
#### Intelligent Caching Strategy
We implement a multi-tier caching strategy optimized for Nuxt applications:
**Cache Headers by Content Type:**
```
# Static assets (JS, CSS, images)
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable
# Pre-rendered pages
Cache-Control: public, max-age=3600, s-maxage=3600
# ISR pages
Cache-Control: public, max-age=300, s-maxage=300, stale-while-revalidate=60
# API routes
Cache-Control: private, max-age=300
# Dynamic pages
Cache-Control: no-cache, must-revalidate
```
**Cache Debugging and Monitoring:**\
Monitor cache performance through browser DevTools and our dashboard:
```
# Response headers show detailed cache status
Cdn-Cache: HIT # Served from edge cache
Cdn-Cache-Region: us-east-1 # Cache region
Age: 1847 # Cache age in seconds
X-Cache-Status: fresh # Cache freshness status
```
### Developer Experience
#### Local Development Compatibility
Your existing development workflow remains completely unchanged. Sherpa.sh works with your current setup without requiring any modifications:
```bash
# Standard Nuxt development commands (unchanged)
npm run dev # Start development server
npm run build # Build for production
npm run preview # Preview production build locally
npm run generate # Generate static site
# Deploy to Sherpa.sh
git add .
git commit -m "Update content"
git push origin main # Triggers automatic deployment
```
#### Build Process Insights
Monitor your Nitro builds in real-time through our comprehensive dashboard:
**Build Analytics:**
* **Build Duration**: Typical Nuxt builds complete in 45-90 seconds
* **Bundle Analysis**: Detailed breakdown of chunk sizes and dependencies
* **Nitro Optimization**: View tree-shaking results and dead code elimination
* **Performance Metrics**: Track build performance over time
**Build Logs:**
```
✓ Nuxt project info
✓ Installing dependencies (npm ci)
✓ Building Nuxt application
✓ Nitro build completed in 52.3s
✓ Analyzing bundle size: 2.1MB total
- Client bundle: 1.4MB
- Server bundle: 0.7MB
✓ Optimizing static assets
✓ Deploying to global edge network
✓ Deployment successful in 1m 23s
```
#### Real-Time Debugging & Monitoring
Access comprehensive logging and monitoring through the Sherpa.sh dashboard:
**Available Logs:**
* **Nitro Server Logs**: SSR rendering performance, errors, and request timing
* **CDN Access Logs**: Static asset delivery metrics and cache hit rates
* **API Route Logs**: Server-side function execution times and error rates
* **Build Logs**: Complete build process with detailed timing information
### Configuration Examples
#### Advanced Route Rules
Configure different behaviors for different parts of your application:
```typescript
// nuxt.config.ts - Comprehensive route configuration
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
routeRules: {
// Homepage - pre-rendered with long cache
'/': {
prerender: true,
headers: { 'cache-control': 'public, max-age=3600' }
},
// Blog section - ISR with sitemap generation
'/blog': { prerender: true },
'/blog/**': {
isr: 3600, // Regenerate hourly
headers: { 'cache-control': 's-maxage=3600' }
},
// Product pages - ISR with SEO optimization
'/products': { prerender: true },
'/products/**': {
isr: 1800, // Regenerate every 30 minutes
headers: {
'cache-control': 's-maxage=1800, stale-while-revalidate=300',
'x-robots-tag': 'index, follow'
}
},
// API routes with CORS and caching
'/api/public/**': {
cors: true,
headers: {
'cache-control': 'public, max-age=300',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE'
}
},
// Private API routes
'/api/private/**': {
headers: { 'cache-control': 'private, no-cache' }
},
// Admin panel - SPA mode with no indexing
'/admin/**': {
ssr: false,
index: false,
headers: {
'cache-control': 'no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate',
'x-robots-tag': 'noindex, nofollow'
}
}
}
}
})
```
#### Environment-Specific Configuration
Handle different environments with flexible configuration:
```typescript
// nuxt.config.ts - Environment-aware configuration
const isDevelopment = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development'
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
export default defineNuxtConfig({
// Development vs Production settings
ssr: isProduction, // SSR in production, SPA in development for faster dev
nitro: {
preset: isProduction ? 'node-server' : 'dev',
minify: isProduction,
sourceMap: !isProduction
},
// Runtime configuration
runtimeConfig: {
// Private keys (only available server-side)
apiSecret: process.env.API_SECRET,
databaseUrl: process.env.DATABASE_URL,
// Public keys (exposed to client-side)
public: {
apiBase: process.env.NUXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE ||
(isProduction ? 'https://api.yourapp.com' : 'http://localhost:3001'),
siteUrl: process.env.NUXT_PUBLIC_SITE_URL ||
(isProduction ? 'https://yourapp.com' : 'http://localhost:3000'),
gtmId: process.env.NUXT_PUBLIC_GTM_ID || ''
}
},
// Environment-specific modules
modules: [
'@nuxtjs/tailwindcss',
...(isProduction ? ['@nuxtjs/robots'] : [])
]
})
```
#### Custom Headers and Security
Implement comprehensive security headers for production applications:
```typescript
// nuxt.config.ts - Security-focused configuration
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
routeRules: {
'/**': {
headers: {
// Prevent clickjacking
'X-Frame-Options': 'DENY',
// Prevent MIME type sniffing
'X-Content-Type-Options': 'nosniff',
// Referrer policy
'Referrer-Policy': 'strict-origin-when-cross-origin',
// Permissions policy
'Permissions-Policy': 'camera=(), microphone=(), geolocation=()',
// Content Security Policy
'Content-Security-Policy': [
"default-src 'self'",
"script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://www.googletagmanager.com",
"style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://fonts.googleapis.com",
"font-src 'self' https://fonts.gstatic.com",
"img-src 'self' data: https:",
"connect-src 'self' https://api.yourapp.com"
].join('; ')
}
}
}
}
})
```
### Troubleshooting
#### Common Issues and Solutions
**Build Failures:**
* **Node.js Version**: Ensure Node.js 18+ is specified in your `package.json` engines field
* **Dependencies**: Check for missing dependencies or version conflicts in `package.json`
* **Memory Issues**: Large applications may need increased memory limits in build settings
* **Nitro Preset**: Verify Nitro preset compatibility with your deployment requirements
```json
// package.json - Specify Node.js version
{
"engines": {
"node": ">=18.0.0",
"npm": ">=8.0.0"
}
}
```
#### Getting Help
**Documentation Resources:**
* **Comprehensive Guides**: [docs.sherpa.sh](https://sherpa-sh.gitbook.io/sherpa.sh-docs)
* **API Reference**: Detailed API documentation for advanced configurations
* **Best Practices**: Performance optimization guides and security recommendations
**Support:**
* **Discord Community**: Join our [Discord server](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy) for real-time help
* **Support Tickets**: Join our [Discord server](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy) for submitting private support tickets
Ready to deploy your Nuxt.js application? [Create a free account →](https://app.sherpa.sh/auth/sign-up)
# Remix
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
Deploy Remix Applications with sherpa.sh
# Remix
Host your full-stack Remix applications with zero configuration, significantly lower costs, and higher performance. Our platform is purpose-built for modern web frameworks, delivering superior performance at a fraction of the price of traditional cloud providers by utilizing our own dedicated servers.
### Why sherpa.sh is Perfect for Remix Applications
#### Massive Cost Savings on Server-Side Rendering
Unlike other platforms that charge premium rates for SSR compute time, sherpa.sh offers flat-rate pricing that makes sense for Remix apps:
**Cost Comparison for Typical Remix App:**
```
Monthly Traffic: 500K page loads + 1M API requests
Traditional Cloud Providers:
- Compute time: $180-320/month
- Function invocation fees: $45-80/month
- Bandwidth: $25-40/month
Total: $250-440/month
sherpa.sh:
- Unlimited SSR compute: $0 (included)
- Zero function invocation fees: $0
- Global CDN: $0 (included)
Total: $29/month flat rate
```
#### Zero Edge Request Charges
Remix applications generate numerous requests due to their loader and action architecture:
* Each loader call generates a server request
* Form submissions trigger action requests
* Resource routes create additional endpoints
**Real-World Impact:**
* Remix apps average 15-25 requests per user session
* Other platforms charge $0.40 per million requests
* sherpa.sh: $0 for unlimited requests
#### Optimized for Remix Architecture
Our infrastructure is specifically tuned for Remix's unique approach to full-stack React applications:
**Server-Side Rendering Performance:**
* Pre-warmed Node.js instances across regions
* No cold starts for your server entry points
* Intelligent routing based on geographic proximity
**Performance Benchmarks:**
```
SSR response times (95th percentile):
sherpa.sh: 89ms average globally
Traditional VPS: 340ms average
Other serverless: 180ms average (with cold starts)
```
### Quick Start Guide
Get your Remix application deployed in under 3 minutes with automatic configuration detection.
#### Prerequisites
* Remix v2.7+ project
* Git repository (GitHub)
* Node.js 18+ for local development
#### Deployment Steps
1. **Connect Repository**: Link your Git repository to sherpa.sh dashboard
2. **Auto-Detection**: We automatically detect your Remix configuration and build settings
3. **Deploy**: Push to your main branch triggers automatic deployment
4. **Live**: Your app is available at `https://your-app.sherpa.software`
#### What You Get Instantly
* **Zero Configuration**: Works with your existing `vite.config.js`
* **Global CDN**: Static assets served from 200+ edge locations
* **Automatic HTTPS**: SSL certificates provisioned and renewed automatically
* **Performance Optimization**: Built-in asset optimization and caching
* **Flat Rate**: No idle costs - only pay for actual usage
### Platform Optimizations
#### Automatic Configuration Enhancements
When you deploy to sherpa.sh, we make minimal but powerful optimizations to maximize performance:
**Environment Variables Set Automatically:**
```bash
NODE_ENV=production
PORT=3000
ORIGIN=https://your-domain.com
PROTOCOL_HEADER=x-forwarded-proto
HOST_HEADER=x-forwarded-host
```
**Asset URL Optimization:**
```javascript
// Your remix.config.js gets enhanced with:
export default {
// Your existing configuration preserved
publicPath: "https://your-app.sherpa.software/{hash}/",
// Benefits:
// - Global CDN delivery
// - Instant rollbacks via hash versioning
// - Long-term caching with cache busting
};
```
#### Performance Features
**Code Splitting Optimization:**
* Remix's automatic code splitting works perfectly with our HTTP/2 infrastructure
* Route-based chunks load in parallel with zero additional configuration
* Intelligent prefetching for faster navigation
**Static Asset Acceleration:**
* Automatic Brotli and Gzip compression
* Long-term caching for unchanged files
* Edge caching for <50ms global load times
**Caching Strategy:**
```
Cache-Control Headers (automatically applied):
- Static assets (JS, CSS): public, max-age=31536000, immutable
- Server responses: Based on your loader configurations
- API routes: Respect your custom cache headers
```
#### Database Integration
**Automatic Optimizations:**
* Connection pooling tuned for Remix patterns
* Regional database placement matching your deployment
* Environment variable management for database URLs
**Managed Databases (optional):**
* PostgreSQL
* MySQL
* MongoDB
### Developer Experience
#### Local Development Compatibility
Your existing Remix development workflow remains completely unchanged:
```bash
# Development (unchanged)
npm run dev
# Build locally (unchanged)
npm run build
# Deploy to sherpa.sh
git push origin main # Triggers automatic deployment
```
#### Build Process Insights
Monitor your deployments in real-time through the dashboard:
* **Build Time**: Typical Remix builds complete in 60-120 seconds
* **Bundle Analysis**: See which routes contribute to bundle size
* **Deployment Status**: Real-time updates on build progress
#### Monitoring & Debugging
**Real-Time Application Logs:**
* Live server console output
* Route-specific performance metrics
* Database query timing
* Asset loading performance
**Performance Insights:**
* Loader execution times per route
* Server response times by geographic region
* CDN cache hit rates
* Bundle size analysis and trends
### Configuration Examples
#### Custom Domain Setup
```javascript
// In your remix.config.js
export default {
// Your existing config remains unchanged
// sherpa.sh automatically handles:
// - SSL certificate provisioning
// - DNS configuration
// - CDN routing
};
```
#### Environment-Specific Variables
Set environment variables directly in the sherpa.sh dashboard:
```bash
# Production environment
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://...
SESSION_SECRET=your-secret-key
API_KEY=your-api-key
# Staging environment
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://staging...
SESSION_SECRET=staging-secret
API_KEY=staging-api-key
```
### Migration Guide
#### From Other Platforms
**Key Migration Steps:**
1. **Repository Connection**: Link your existing Git repository
2. **Environment Variables**: Transfer environment variables via dashboard
3. **Custom Domain**: Configure your production domain
4. **Database**: Update connection strings if needed
#### Build Configuration Compatibility
Sherpa.sh works with standard Vite configurations supported by Remix 2.7 and onward.
### Enterprise Features
#### Advanced Performance
* **100% Uptime SLA**: Financial backing for service availability
* **Custom Edge Logic**: Run code at 200+ global locations
* **Dedicated Infrastructure**: Isolated compute for enterprise workloads
#### Team Collaboration
* **Role-Based Access**: Granular deployment permissions
* **Audit Logging**: Complete deployment history tracking
* **Multiple Environments**: Staging, production, and custom environments
#### Support & Monitoring
* **24/7 Monitoring**: Automated performance tracking
* **Priority Support**: Direct access to platform experts
* **Custom Integrations**: Connect with existing DevOps workflows
### Troubleshooting
#### Common Issues
**Build Failures:**
* Check Node.js version compatibility (18+ required)
* Verify all dependencies are listed in package.json
* Review build logs in deployment dashboard
**Route Issues:**
* Ensure your routes follow Remix file-based routing conventions
* Check for conflicting route patterns
* Verify loader and action exports are properly configured
**Performance Issues:**
* Monitor loader execution times in dashboard
* Check database connection region vs deployment region
* Review asset bundle sizes for optimization opportunities
#### Getting Help
* **Documentation**: Comprehensive guides in our [Documetation](https://sherpa-sh.gitbook.io/sherpa.sh-docs)
* **Support**: Join our [Discord community](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
### Next Steps
After deploying your first Remix application:
1. **Custom Domain**: Connect your production domain in the dashboard
2. **Environment Variables**: Configure secrets and API keys securely
3. **Team Access**: Invite collaborators with appropriate permissions
4. **Monitoring Setup**: Configure alerts for performance and errors
5. **Database Optimization**: Fine-tune connection settings and regions
Ready to deploy your Remix app with better performance and lower costs? [Create your free account →](https://sherpa.sh/signup)
# React
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# React
## React Documentation for Sherpa.sh
We've built sherpa.sh specifically with React developers in mind. As developers who use React daily ourselves, we've optimized every aspect of our platform to make your React apps fly.
### Why React on Sherpa.sh?
We've felt the pain of configuring servers for React apps, uploading files to S3 Buckets, Configuring cache policies, and wrestling with build optimizations, and managing state across distributed systems. So we built something better.
### React Quickstart
Get your React app deployed in under 2 minutes with zero configuration headaches. We've eliminated all the typical setup friction so you can focus on what matters - your code.
#### Out of the box, your React app gets:
* Server-side rendering optimized specifically for React's architecture
* Automatic code splitting and bundle optimization
* Built-in React DevTools support in development environments
* React-aware caching strategies that understand component boundaries
### React Performance Optimizations
We've studied the React rendering lifecycle extensively and built our infrastructure to complement it perfectly:
* **Selective Hydration**: We intelligently prioritize the hydration of interactive components
* **React Compiler Support**: Full support for the latest React compiler optimizations
* **Streaming SSR**: Optimized for React's component model to deliver content faster
* **Component-Level Caching**: Our caching system understands React components and their dependencies
### React Development Experience
We believe building React apps should be joyful, not frustrating:
* **Hot Module Replacement**: Zero-config HMR that preserves component state during development
* **Component Error Handling**: Intelligent error boundaries that provide useful debugging information
* **State Persistence**: Optional persistence of development state between refreshes
* **React-Aware Logging**: Console outputs that understand React's component hierarchy
### Enterprise React Support
Our team includes React core contributors who understand the framework at its deepest levels:
* Dedicated React performance tuning for large-scale applications
* Custom hook development for your specific business requirements
* Advanced state management solutions for complex enterprise applications
* React architecture consultation from experts who've scaled massive React applications
We're a lean team of React enthusiasts, focused on creating straightforward, powerful solutions that cut through the noise. No fancy marketing, no complicated pricing tiers - just real tools built by people who understand the craft.
Our mission isn't about selling a platform. It's about empowering React developers to turn their ideas into reality.
# Supported AI Website Builders
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Supported AI Website Builders
At Sherpa.sh, we've built a framework detection system that automatically detects and optimizes deployments of websites build with AI tools like Bolt.new and Loveable.\
\
When you connect your repository or upload your files, our system performs a thorough analysis to identify the underlying technology stack.
> ```
> "Is it Lovable? Is it Bolt? Is it some other AI creation?
> Don't worry - we'll figure it out while you grab coffee."
> ```
Our auto-detection process examines:
* File structure patterns
* Configuration files
* Dependencies and import statements
* Build artifacts and metadata
Once identified, we automatically configure the optimal deployment settings for your specific AI builder, so you don't have to become an expert in deployment configurations that would make NASA engineers weep.
### Supported Builders
* **Rapid MVPs & Full-Stack:** Bolt.new, Base44, Codev, Softgen, Bubble, Replit, MagicPatterns, Vercel v0
* **Design/Prototyping Focus:** Banani, Stitch, WeWeb, MagicPath, Uizard, Dora, Framer
* **No-Code Simplicity:** Buildglare, Jimdo, Hostinger, Wix, Squarespace
* **Developer Oriented:** Cursor, Vercel v0, Builder.io, MagicPatterns, Replit
### Why Sherpa.sh For AI-Generated Sites
AI website builders create impressive sites quickly, but production deployment introduces complexities these tools don't address. Here's where we come in:
#### Performance Amplification
We've studied how AI tools generate code and built specific optimizations to address their common patterns. Your AI-generated site will actually run _faster_ on our platform than on generic hosting. We will ship your assets all around the world, running multiple copies of your application ensuring your users get lightning fast loads times, no matter where in the world they live.
#### Scale Without Tears
AI-generated websites often struggle under heavy traffic. Our infrastructure automatically scales to handle sudden traffic spikes without turning your beautiful site into a digital paperweight.
### Getting Started
1. Connect your GitHub repository or upload your files
2. Our system detects your AI builder automatically
3. We deploy with optimized settings
4. You look like a deployment genius to your team
No configuration files to edit. No infrastructure puzzles to solve.
> ```
> "The most impressive part of your AI website shouldn't be
> that you managed to deploy it successfully."
> ```
**Go build something amazing. We'll handle the rest.**
# Sveltekit
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Sveltekit
Deploy your SvelteKit applications with zero configuration and enterprise-grade performance. Our platform is specifically optimized for SvelteKit's architecture, delivering faster builds and better runtime performance than traditional hosting solutions.
### Why sherpa.software is Perfect for SvelteKit
#### Zero Edge Request Charges
Unlike other platforms that charge per edge request, we never bill for edge traffic. This matters for SvelteKit because of its intelligent code-splitting strategy:
```javascript
SvelteKit automatically creates many small chunks
// app.js (5kb) - Core application logic
// chunk-abc123.js (2kb) - Home page component
// chunk-def456.js (3kb) - About page component
// chunk-ghi789.js (1kb) - Shared utilities
```
**Why This Saves You Money:**
* SvelteKit creates 20-50+ small JavaScript chunks per application (or more!)
* Each chunk loads on-demand, triggering separate edge requests
* Other platforms charge $0.01-0.10 per 10,000 edge requests
* **With sherpa.software: $0.00 for unlimited edge requests**
**Real-World Impact:**
SvelteKit App Monthly Traffic Overview
Static Assets: Approximately 2 million requests for JS chunks, CSS, and images
SSR Pages: Approximately 500,000 requests
API Calls: Approximately 1 million requests
Cost Comparison
Other Platforms: $150-300/month in edge fees
Sherpa.sh: $0
#### Optimized Node.js Adapter Performance
We've fine-tuned our infrastructure specifically for `@sveltejs/adapter-node` to deliver optimal SSR performance:
**SSR Performance Optimizations**
* **Cold Start Elimination**: Pre-warmed Node.js instances across regions
* **Memory Optimization**: 512MB-2GB+ containers with intelligent horizontal scaling
* **Request Routing**: Smart load balancing based on geographic proximity
**Performance Benchmarks:**
# SSR response times (95th percentile)
sherpa.software: 89ms average globally
Traditional VPS: 340ms average
Other serverless: 180ms average (with cold starts)
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
### Quick Start Guide
Get your SvelteKit app live in under 2 minutes with our streamlined deployment process.
#### Prerequisites
* SvelteKit 2.x project
* Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket)
* Node.js 18+ locally for development
#### Deployment Steps
1. **Connect Repository**: Link your Git repository to sherpa.software
2. **Auto-Detection**: We automatically detect your SvelteKit configuration
3. **Deploy**: Push to your main branch triggers automatic deployment
4. **Live**: Your app is available at `https://your-app.sherpa.software`
#### What You Get Instantly
* **Zero Configuration**: Works with your existing `svelte.config.js`
* **Global CDN**: Static assets served from 200+ edge locations
* **Automatic HTTPS**: SSL certificates provisioned and renewed automatically
* **Performance Optimization**: Built-in code splitting and asset preloading
* **Pay-per-Use**: No idle costs - only pay for actual usage
:::note
**By default CDN caching is on:** This means you need to [set cache-control headers](https://svelte.dev/tutorial/kit/headers) on pages that you don't want to be cached. Such as login pages. Please see our [CDN Docs](/infrastructure/cdn-and-caching/) for more info on cache-control headers.
:::
### Configuration
#### Server-Side Rendering Configuration
For server-side rendering, you must use the `@sveltejs/adapter-node` adapter with `trustProxy: true`:
```bash
# Install the Node adapter
npm install @sveltejs/adapter-node
```
```js
// svelte.config.js
import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-node';
export default {
kit: {
adapter: adapter({
out: 'build',
trustProxy: true // Required for proper load balancer header handling
})
}
};
```
:::note
**For SSR deployments:** The `trustProxy: true` option is required to properly handle load balancer headers for HTTPS detection and host handling.
:::
#### Static Site Generation Configuration
For static site generation, use the `@sveltejs/adapter-static` adapter:
```bash
# Install the Static adapter
npm install @sveltejs/adapter-static
```
```js
// svelte.config.js
import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-static';
export default {
kit: {
adapter: adapter({
pages: 'build',
assets: 'build',
fallback: undefined,
precompress: false
})
}
};
```
**Environment Variables Set Automatically**
```bash
PORT=3000 # Standard runtime port (SSR only)
ORIGIN=https://your-domain.com # Your custom domain
NODE_ENV=production # Production optimizations
PROTOCOL_HEADER=x-forwarded-proto # HTTPS detection
HOST_HEADER=x-forwarded-host # Proper host handling
```
#### Performance Enhancements
**Code Splitting Optimization**
SvelteKit's automatic code splitting works perfectly with our HTTP/2 infrastructure:
**Parallel Chunk Loading in Routes**
Your route-based chunks load in parallel, requiring no additional configuration—this functionality works automatically.
**Static Asset Acceleration**
* **File Hashing**: Long-term caching for unchanged files
* **Compression**: Automatic Brotli and Gzip compression
* **Edge Caching**: Assets cached globally for <50ms load times
**Prerendering Support**
To enable prerendering in your routes, use the following snippet:
```javascript
// In routes that can be prerendered:
export const prerender = true;
// These routes are built as static HTML and
```
### Advanced Features
#### Image Optimization
Automatic image optimization with SvelteKit's enhanced:img component:
```svelte
svelte
```
**Optimization Features:**
* WebP/AVIF conversion for modern browsers
* Responsive sizing based on device
* Lazy loading below the fold
* Global CDN delivery
#### Caching Strategy
**Intelligent Cache Headers**
We will use whatever cache-headers you set in Sveltekit setup, otherwise default to these.
```bash
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable # Static assets (JS, CSS, images)
Cache-Control: public, max-age=3600 # Prerendered pages
Cache-Control: no-cache # API routes
```
**Cache Debugging**
Check cache performance in browser DevTools:
```bash
# Response headers show cache status
Cdn-Cache: HIT # Served from edge cache
Cdn-Cache: MISS # Fetched from origin
```
#### Load Balancing & Scaling
**Server-Side Rendering (SSR)**
* Auto-scaling Node.js instances
* Geographic distribution for reduced latency
* Zero-downtime deployments
### Developer Experience
#### Local Development Compatibility
Your local development workflow remains unchanged:
```bash
# Development (unchanged)
npm run dev
# Build locally (unchanged)
npm run build
# Deploy to sherpa.software
git push origin main # Triggers automatic deployment
```
#### Build Process Insights
Monitor your builds in real-time:
* **Build Time**: Typical SvelteKit builds complete in 30-60 seconds
* **Bundle Analysis**: See which routes contribute to bundle size
#### Debugging & Monitoring
**Real-Time Logs**
View live application logs from inside the portal. You get logging for:
* **CDN requests**
* **Live Node Console**
### Configuration Examples
#### Custom Headers
Add custom headers for specific routes in your SvelteKit configuration:
```javascript
// In your svelte.config.js
import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-node';
export default {
kit: {
adapter: adapter({
out: 'build',
trustProxy: true
}),
// Add custom headers for specific routes
headers: {
'/**': {
'X-Frame-Options': 'DENY',
'X-Content-Type-Options': 'nosniff'
}
}
}
};
```
#### Environment-Specific Configuration
```javascript
// Different configs per environment
import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-node';
const config = {
kit: {
adapter: adapter({
out: 'build',
trustProxy: true
}),
paths: {
base: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '/app' : ''
}
}
};
export default config;
```
### Enterprise Features
#### Advanced Security
* **SOC 2 Compliance**: Enterprise-grade security controls
* **Custom WAF Rules**: Protect against application-specific threats
* **DDoS Protection**: Automatic traffic filtering and rate limiting
#### Performance & Reliability
* **100% Uptime SLA**: Guaranteed uptime with financial backing
* **Custom Edge Logic**: Run code at 200+ global locations
* **Dedicated Infrastructure**: Isolated compute for enterprise workloads
#### Developer Support
* **Dedicated Account Manager**: Direct line to platform experts
* **Priority Support**: <2 hour response time for critical issues
* **Custom Integrations**: Connect with your existing DevOps tools
### Troubleshooting
#### Getting Help
* **Documentation**: Comprehensive guides here
* **Community Support & Tickets**: Join our [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/Pn7N2Wwbjy)
### Migration Guide
#### From Other Platforms
The easiest way to migration from another platform is to follow the [quickstart guide](#quick-start-guide).
* [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
* [Connect Github](../../getting-started/quickstart#step-2-link-your-github)
* [Configure your application settings](../../getting-started/configuration)
#### From Self-Hosted
Key differences when migrating from self-hosted SvelteKit:
* **Adapter Requirement**: Use `@sveltejs/adapter-node` with `trustProxy: true` for SSR, or `@sveltejs/adapter-static` for static sites
* Remove PM2 or Docker configurations
* Environment variables managed in dashboard
* No need for reverse proxy setup
* Automatic SSL certificate management
### Next Steps
After deploying your first SvelteKit app:
1. **Custom Domain**: Connect your domain in the dashboard
2. **Environment Variables**: Configure secrets and API keys
3. **Team Access**: Invite collaborators with role-based permissions
4. **Monitoring**: Set up alerts for performance and errors
5. **API Integration**: Connect to databases and external services
Ready to deploy? [Create a free account →](https://sherpa.software/auth/sign-up)
# Lesson 1: Deploying your first application
https://docs.sherpa.sh/undefined
undefined
# Lesson 1: Deploying your first application
[Watch Video](https://youtu.be/-RhWwr9xy48)